Thermal Properties Of Matter
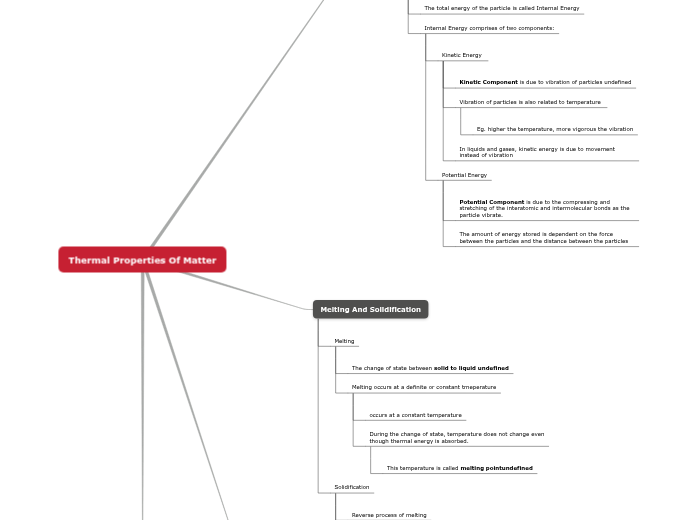
Internal Energy
What is Internal Energy?
Particles in a solid held together by strong interatomic or intermolecular bonds, and vibrate in a fix position.
The total energy of the particle is called Internal Energy
Internal Energy comprises of two components:
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic Component is due to vibration of particles
Vibration of particles is also related to temperature
Eg. higher the temperature, more vigorous the vibration
In liquids and gases, kinetic energy is due to movement instead of vibration
Potential Energy
Potential Component is due to the compressing and stretching of the interatomic and intermolecular bonds as the particle vibrate.
The amount of energy stored is dependent on the force between the particles and the distance between the particles
Melting And Solidification
Melting
The change of state between solid to liquid
Melting occurs at a definite or constant tmeperature
occurs at a constant temperature
During the change of state, temperature does not change even though thermal energy is absorbed.
This temperature is called melting point
Solidification
Reverse process of melting
The change of state between a liquid to a solid