UNIT 1: Biochemistry
Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Function of Carbohydrates:

-Get ATP -structure: part of cell wall and form part of DNA and RNA backbone -ID markers and communicators: in cell membrane linked to proteins and lipids
Monosaccharides
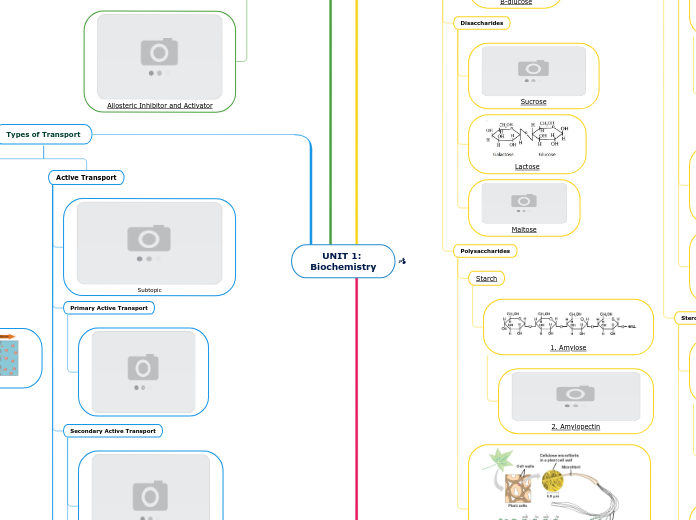
Fructose
B-galactose
Ribose

α-glucose
Deoxyribose
B-glucose
Disaccharides

Sucrose
Lactose

Maltose
Polysaccharides
Starch

1. Amylose

2. Amylopectin
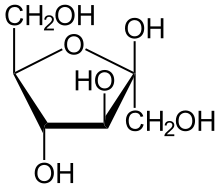
Cellulose
Lipids
Function of Lipids:

-Storing energy: change carbs into fat and store the fat molecules as droplets in fat tissues -Insulation: A layer of fat under the skin -Building: membranes (phospholipid layers) and other cell parts -Chemical signalling molecules (hormones)
Types of Fatty acids

Saturated and unsaturated fatty acid
Cis Vs Trans
Triglycerides

Phospholipids

Structure of a Phospholipid
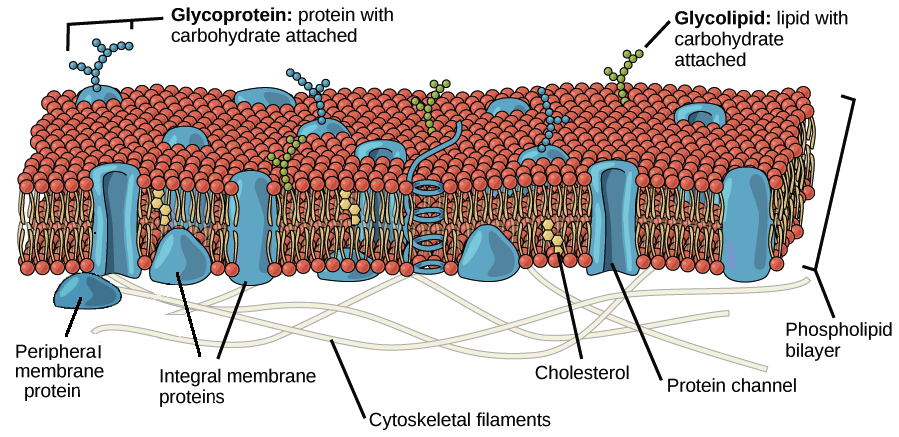
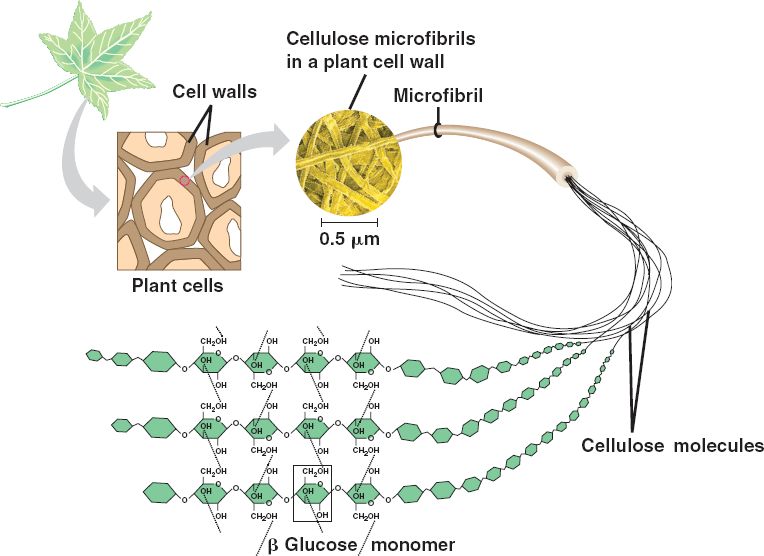
Phospholipid Bilayer

Micelle

Liposomes
Steroids

Cholesterol

Cholesterol
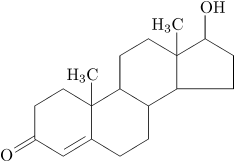
Testosterone
Proteins
Function of Proteins:

-the most complex molecule in living organisms
-used as structural building blocks and functional molecules and are involves in almost everything that cells do
Monomers of Protein

Amino Acid
Glycine
Peptide Bond

Structure pf Protein

Primary, Secondary, and Quaternary structure in Proteins
Nucleic Acid
Function of
Nucleic Acid:
-informational nucleotides
-used by all organisms to produce identical copies of themselves which means that they can reproduce
instruction code of organism is stored along the strands of DNA

Nucleotides and Purine and Pyrimidines
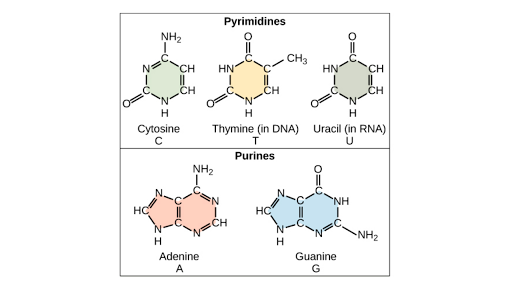
DNA Nucleotide
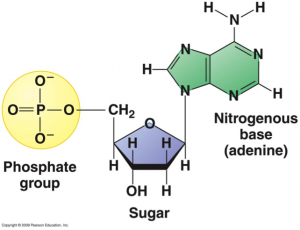
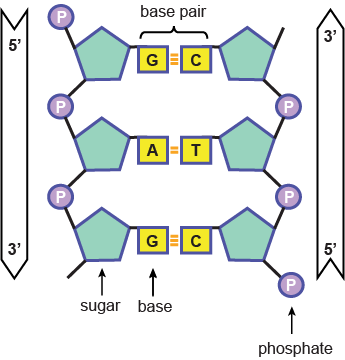
RNA Nucleotide
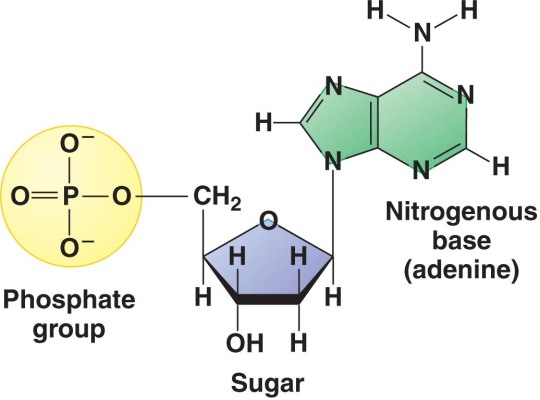

Functional Groups

Methyl

Hydroxyl
Aldehyde
Ketone
Carboxyl
Amine
Phosphate
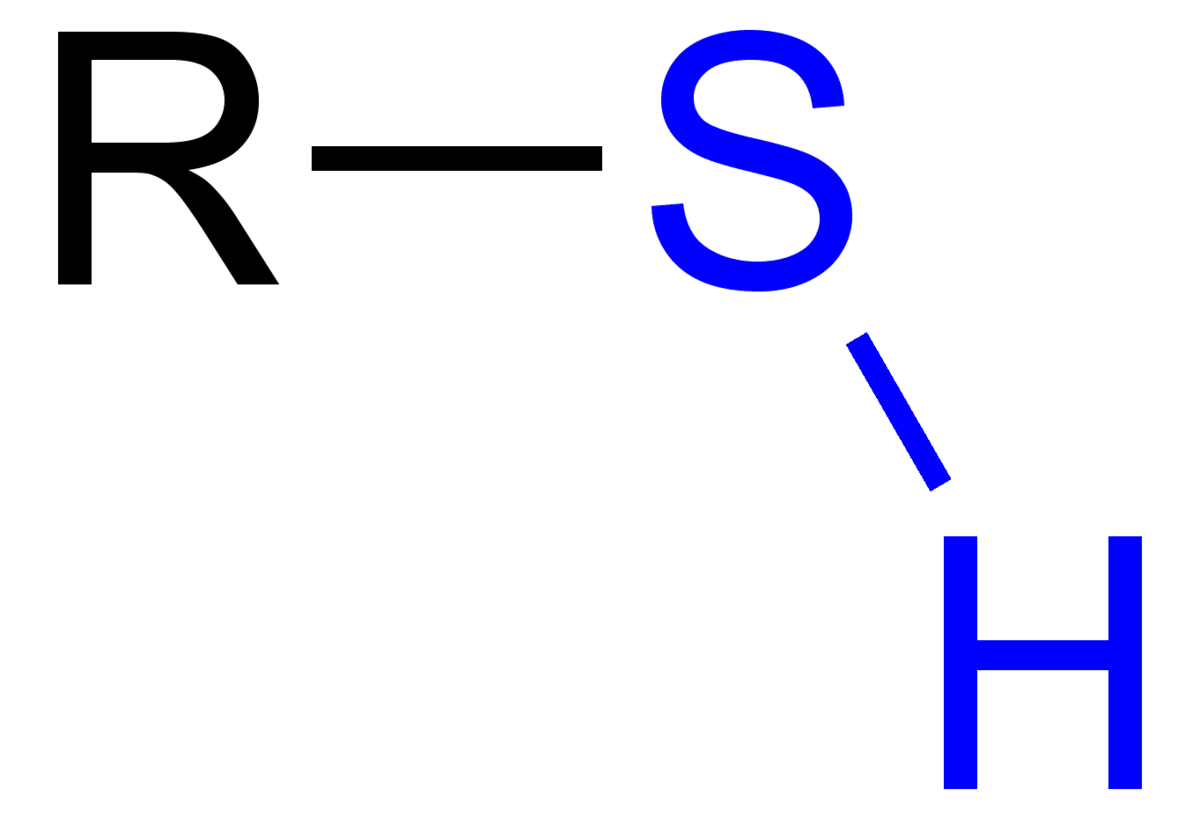
Sulfhydryl
Type of Protein:
Enzymes
Function of
Enzymes:
-proteins made by the body
speed up chemical reactions
- an reaction would happen too slowly and not survive without an enzyme
How enzymes work

Lock and Key Hypothesis (incorrect)
Induced Fit Model (correct)
Effects on Enzyme Activity

1. Saturation

2. Temperature

3. pH
Enzyme Regulation

Allosteric Inhibitor and Activator
Types of Transport
Passive Transport

Simple Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion

Channel Protein

Carrier Protein
Osmosis

Active Transport

Subtopic
Primary Active Transport

Secondary Active Transport

Symport

Antiport
1. Exocytosis
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_process-5ae370b4a9d4f900373c9b48.jpg)
2. Endocytosis

1. Phagocytosis

2. Pinocytosis

Receptor-Assisted Endocytosis