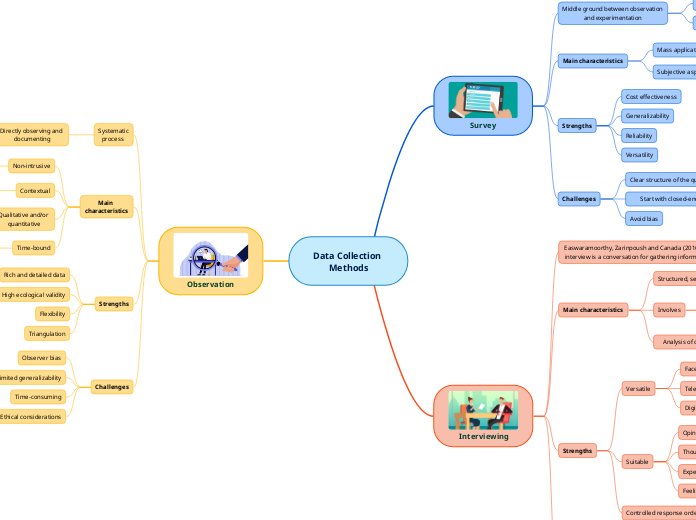
Data Collection Methods
Observation
Ethical considerations
Time-consuming
Limited generalizability
Observer bias
Triangulation
Flexibility
High ecological validity
Rich and detailed data
Time-bound
Specific time periods
Qualitative and/or quantitative
Qualitative aspects & Quantitative data
Contextual
Contextual information
Non-intrusive
External observation
Systematic process
Directly observing and documenting
Behaviors, events, or phenomena
Interviewing
Challenges
Time consuming
Never 100% anonymous
Subconscious bias
Responses cannot be generalized
Ineffective
Population is unwilling to answer
Controlled response order
Suitable
Feelings
Experiences
Thoughts
Opinions
Versatile
Digital tool
Telephone
Face-to-face
Analysis of complex questions and considerable probing
Involves
Interviewee
Interviewer
Structured, semi-structured or unstructured
Easwaramoorthy, Zarinpoush and Canada (2016): "An interview is a conversation for gathering information"
Survey
Challenges
Avoid bias
Start with closed-ended questions and end with open-ended questions
Clear structure of the questions
Strengths
Versatility
Reliability
Generalizability
Cost effectiveness
Main characteristics
Subjective aspects
Mass application
Large data set
Middle ground between observation and experimentation
Absence of which the participant is questioned
Observed situations are recorded