da Alexia Rivera mancano 2 anni
241
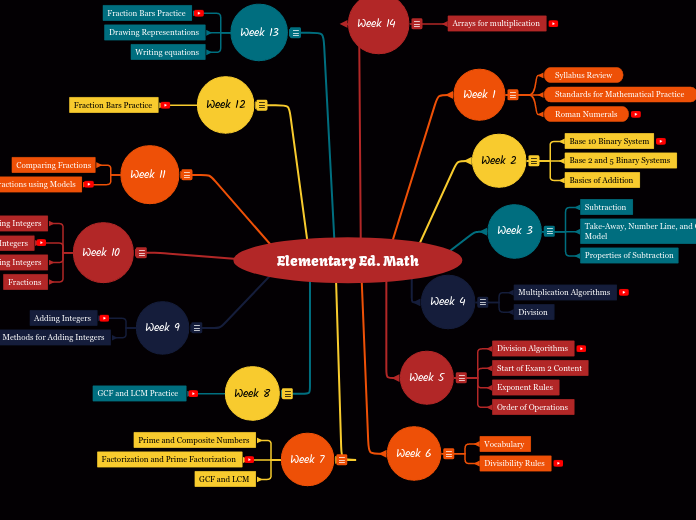
Elementary Ed. Math
da Alexia Rivera mancano 2 anni
241

Più simili a questo
Vocabulary:
A number can be both composite AND square
1 is not Prime or Composite
Methods to find Greatest Common Factor and Least Common Multiple :
1.) Intersection of Sets
2.) Prime Factorization Method
3.) Venn Diagram Method
Used GCF and LCM to solve Word Problems
Vocabulary:
Integer Addition Methods:
Model for Multiplying Integers:
Dividing Integers:
Fraction Parts:
numerator- how many of the whole we are talking about
denominator- how many pieces in the whole
Proper Fraction:
The numerator is smaller then the denominator
Improper Fraction:
The numerator is larger than the denominator
Equivalent Fractions:
Represent the same value, but use different numbers/size pieces
Comparing Fractions:
Same Denominator/ Same Size Pieces-
Same Numerator/Same Number of Pieces-
-The bigger the denominator, the smaller the pieces
-The smaller the denominator, the bigger the pieces
In class practice drawing models for mixed numbers and improper fractions.
Sums and Differences of fractions using fraction bars as models.
IN CLASS PRACTICE
Fraction Bars Practice with Irregular Fractions
Practice with drawing representations and equations to solve word problems
Vocabulary:
Divisibility Rules:
2: A number is divisible by 2 if the units( ones) digit is even
EX: 254--------> 4 is even
3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sun of the digits is divisible by
EX: 2,571--------> 2+5+7+1=15 --------> 15 is divisible by 3
6: A number is divisible by 6 if the number is divisible by both 2 and 3
9: A number is divisible by 9 if the sum of the digits is divisible by 9.
EX: 720,936--------> 7+2+0+9+3+6=27--------> 27/9=3
5:A number is divisible by 5 if the units (ones) digit is divisible by 5
EX:2505--------> 5 is divisible by 5
10: A number is divisible by 10 if the units(ones) digit is divisible by 10
EX: 67830--------> 0/10=0
4: A number is divisible by 4 if the last two digits is a number that is divisible by 4.
EX: 344--------> 44/4=11
8: A number is divisible by 8 if the last 3 digits is a number that is divisible by 8.
EX: 2568--------> 568/8=71
11: A number is divisible by 11 if the sum of the odd power of 10 digits minus the sum of the even powers of 10 digits is divisible by 11
EX: 9482--------> (8+9) - (2+4)= 6-17=-11--------> -11/11=-1
7:No rule, Try division
Algorithms for division
Start of Exam 2 Content:
Exponent Rules:
Power of a Power Rule:
Same Exponents:
Order of Operations:
Parenthesis ( ), Brackets [ ], Braces { }
Exponents
Multiplication
Division
Addition
Subtraction
How would you explain odd numbers and even numbers to students?
Algorithms of Multiplication
-Standard Algorithm: Multiplying in Parts
-Expanded Algorithm: When doing multi-digit multiplication, separate the tens and ones and multiply.
EX: 35 X 15 --------------> 30 + 5
x10 + 5
525
-Partial Products: Multiply the digits in the ones place first and bring the answer down. Now multiply the digit in the ones place with the digit in the tens place and bring it below as well. Add the results of both together.
23 X 4 ----------------> 23
x 4
12
+80
92
-Division:
Properties of Division that DO NOT hold:
-Subtraction: Taking away # from the Sum
-Take Away Model: Show using Chips/Coins/ Cubes
-Number Line Model
-Comparison Model:
"Sara is 3 feet tall. Her older brother is 5 feet tall. How much taller is Sara's older brother?"
-Missing Addend Model:
6 = 4 + ______
6 - 4 = 2
Properties of Subtraction that DO HOLD
-Closure Property:
Whole # + Whole # = Unique Whole #
-Identity Property:
5 - 0 = 5 = 0 + 5
-Base 10 Binary System/ Powers of 10
-Base 2 and Base 5 Binary Systems
-Addition:
-Reviewed the Syllabus and designed our ideal classroom.
-Created a poster analyzing Standards for Mathematical Practice "Make Sense of Problems & Persevere In Solving Them".
-Discussion of the Number System and Roman Numerals
Continued practice drawing fractions and models to solve.
Use Arrays to show Multiplication