da LIZETH KATHERINE IPIALES REINA mancano 4 anni
284
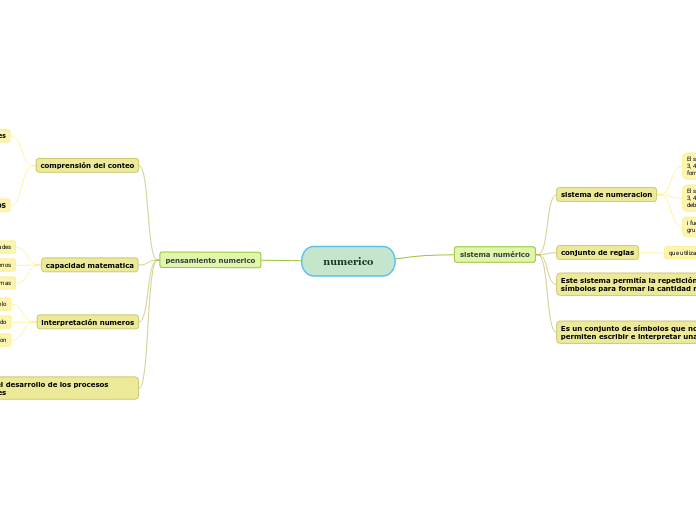
numerico
da LIZETH KATHERINE IPIALES REINA mancano 4 anni
284

Più simili a questo
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
There are four Future tenses:
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Continuous for future actions:
Structure:
Will + Subject + Have Been + Verb-ING
e.g. How long will they be working on that project next week?
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Have Been + Verb-ING
e.g. They won’t have been working on that project for two years next week.
Structure:
Subject + Will Have Been + Verb-ING
e.g. They will have been working on that project for two years next week.
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
Structure:
Will + Subject + Have + Past Participle?
e.g. Will you have met your colleague by this time tomorrow?
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Have + Past Participle
e.g. I won’t have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
Structure:
Subject + Will Have + Past Participle
e.g. I will have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
Future Continuous is used:
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
Structure:
Will + Subject + Be +Verb-ING?
e.g. Will you be having fun at the party?
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Be + Verb-ING
e.g. He won’t be having fun at the party.
Structure:
Subject + Will Be + Verb-ING
e.g. You will be having fun at the party.
Future Simple is used:
'Going to' Future is used:
Some adverbs used with 'Going to' Future:
magnitudes
Structure:
BE + Subject + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb?
e.g. Are you going to read the whole book over the weekend?
pensamiento metrico
Structure:
Subject + BE not + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb
e.g. He isn't going to spend his vacation in Hawaii.
PROCESOS GENERALES RELATIVOS
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb
e.g. She’s going to be a professional dancer when she grows up.
Future Simple with 'will'' is used:
Some adverbs used with Future Simple:
Hacer cómputos de manera fluida y hacer estimaciones razonables.
Structure:
Will + Subject + V1(First Form of Verb)?
e.g. Will you see Mary when she comes back from Denmark?
Comprender el significado de las operaciones y como se relacionan unas con otras.
Structure:
Subject + Won’t (will not) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. You won’t see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
Comprender los números, las formas de representarlos, las relaciones entre ellos y los sistemas numéricos
Structure:
Subject + Will + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I will see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
There are four Present tenses:
Present Perfect Continuous is used:
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect Continuous:
Structure:
Have/ has + Subject + been Verb-ING?
e.g. How long has he been learning German?
Structure:
Subject + haven’t/hasn’t been + Verb-ING
e.g. She hasn’t been playing tennis for a long time.
Structure:
Subject + have/ has been + Verb-ING
e.g. They have been learning French for two years.
Present Perfect is used for:
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
Structure:
Subject + haven’t (have not)/ hasn’t (has not) + Past Participle
e.g. She hasn’t finished the letter.
Structure:
Subject + have/ has + Past Participle (3rd Form of the Verb)
e.g. She has finished the letter.
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
empleando la menor cantidad de palabras y símbolos. inmediatamente superior.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
Form of verb 'to have':
Present Simple is used for:
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
Structure:
Do + Subject (I, You, We, They)+ V1 (First Form of Verb)?
Does + Subject (He, She, It)+V1 (First Form of Verb)?
e.g. Where does he work?
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + do not / don’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
Subject (He, She, It) + does not / doesn’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
e.g. He doesn’t work in a bank.
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.