Theories Explained
By: Gillian Webber
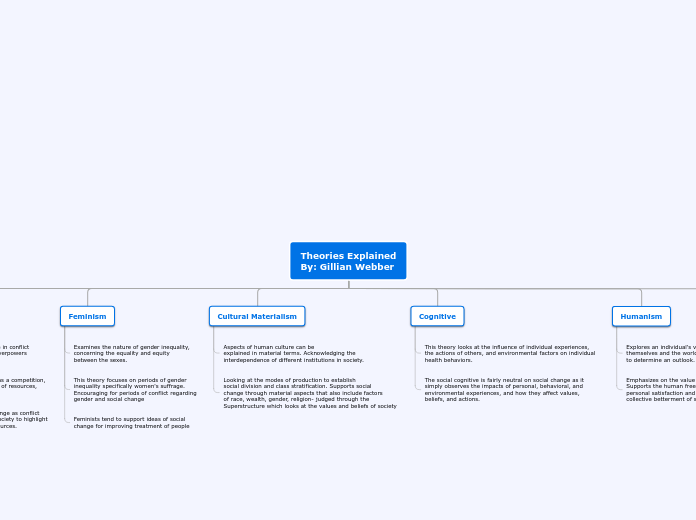
Intersectionality
This theory is highly supportive in the nature of social change and equality among the different social categorizations of class including race, gender, nationality, sexual orientation or disability.
This theory analyzes how different forms of
discrimination overlap (ie, race, gender, religion..)
Examines the multifaceted lives of people, how
people's realities are formed by various factors as
well as the social dynamics that overlap.
Humanism
Emphasizes on the value of humans, alone and collectively. Supports the human freedom and progress to allow for personal satisfaction and happiness to work towards the collective betterment of society.
Explores an individual's view on
themselves and the world around them
to determine an outlook.
Cognitive
The social cognitive is fairly neutral on social change as it simply observes the impacts of personal, behavioral, and environmental experiences, and how they affect values, beliefs, and actions.
This theory looks at the influence of individual experiences, the actions of others, and environmental factors on individual health behaviors.
Cultural Materialism
Looking at the modes of production to establish
social division and class stratification. Supports social
change through material aspects that also include factors
of race, wealth, gender, religion- judged through the Superstructure which looks at the values and beliefs of society
Aspects of human culture can be
explained in material terms. Acknowledging the interdependence of different institutions in society.
Feminism
Feminists tend to support ideas of social
change for improving treatment of people
This theory focuses on periods of gender
inequality specifically women's suffrage.
Encouraging for periods of conflict regarding
gender and social change
Examines the nature of gender inequality,
concerning the equality and equity
between the sexes.
Conflict
This theory supports social change as conflict
serves as a constant state in society to highlight
inequality and redistribute resources.
Conflict theory sees social life as a competition,
and focuses on the distribution of resources,
power, and inequality.
Opposing powers or groups are in conflict
until the more dominant one overpowers
the rest
Structural Functionalist
Integration refers primarily to the ‘adjustment of conflict’. It is concerned with the coordination and mutual adjustment of the parts of the social system
Marx's Theory of Social Change
Social change is a system of integration, as society
grows and changes the way society works and what
it accepts or normalizes
Marx viewed society in material terms of the modes of
production. At a macro level, fitting all parts of society
together as institutional
Durkheim's Social Action Theory
This theory views social change as deviance and disruptive to the process of society as a whole, connected group
This theory is resistant to change, and would view poverty,
as a functional part of society by creating a group of people
that will always need work- despite the issues it causes
"Functionalism sees social structure or the organisation of society as more important than the individual."