da Ivy Nguyen mancano 4 anni
476
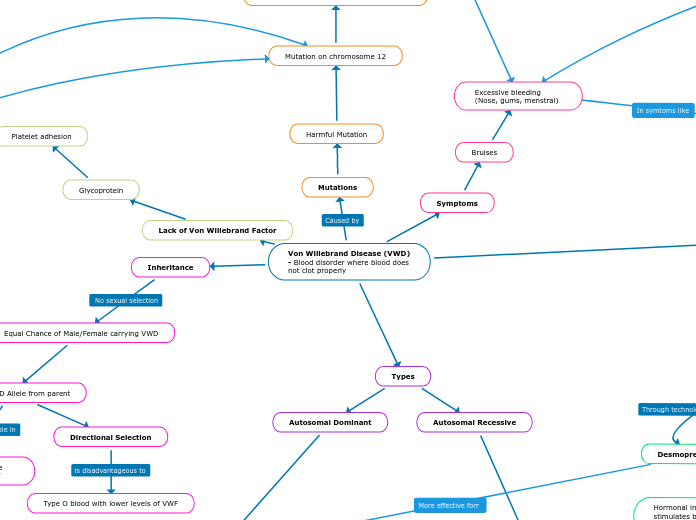
Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) - Blood disorder where blood does not clot properly
da Ivy Nguyen mancano 4 anni
476

Più simili a questo
Rarest, most severe
Mildest, most common
Pseudogene duplicated on chromosome 22
Lack of Von Williebrand Factor (VWF)
Inability to make proper blood clots
Directional Selection
Type O blood with lower levels of VWF
Types A, B, AB blood have higher levels of the VWF
Antifibrinolytics
Drugs that blood clots to breakdown
VWF infusions
Receive regular VWF infusions
Desmopressin (1977)
Hormonal injection that stimulates body to create more VWF in blood vessels
Breeding Dogs
Spontaneous hemorrhages
Shetland Sheepdogs
Scottish Terriers
Doberman Pinscher
In 1960s, combined with factor FVIII and plasma responsible for platelet adhesion
In 1970s, found Ristocetin to induce platelet aggregation