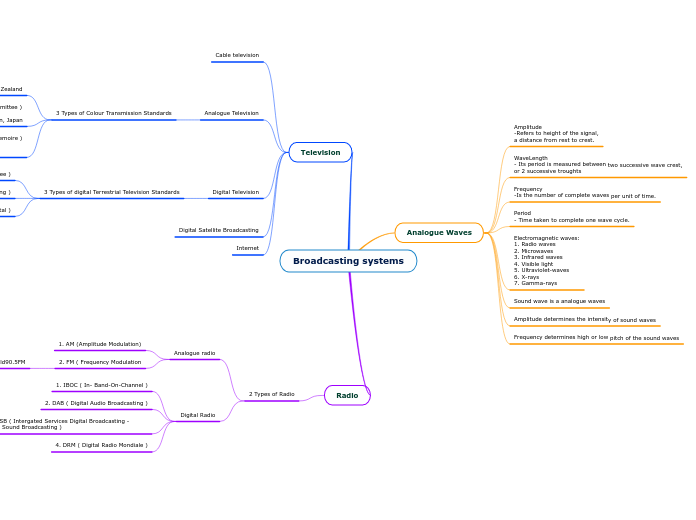
Broadcasting systems
Analogue Waves
Amplitude
-Refers to height of the signal,
a distance from rest to crest.
WaveLength
- Its period is measured between two successive wave crest,
or 2 successive troughts
Frequency
-Is the number of complete waves per unit of time.
Period
- Time taken to complete one wave cycle.
Electromagnetic waves:
1. Radio waves
2. Microwaves
3. Infrared waves
4. Visible light
5. Ultraviolet-waves
6. X-rays
7. Gamma-rays
Sound wave is a analogue waves
Amplitude determines the intensity of sound waves
Frequency determines high or low pitch of the sound waves
Television
Cable television
Analogue Television
3 Types of Colour Transmission Standards
PAL ( Phase Alternating Line )
Countries like:
etc. Australia, China, India, New Zealand
NTSC ( National Television System Committee )
Counteries like:
etc. North America, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan
SECAM ( Sequential Couleur avec Memoire )
Countries like:
etc. Syria, Benin.
Digital Television
3 Types of digital Terrestrial Television Standards
ATSC ( Advanced Television Systems Committee )
DVB ( Digital Video Broadcasting )
ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital )
Digital Satellite Broadcasting
Internet
Radio
2 Types of Radio
Analogue radio
1. AM (Amplitude Modulation)
2. FM ( Frequency Modulation
E.g Class95FM, 98.7FM, Gold90.5FM
Digital Radio
1. IBOC ( In- Band-On-Channel )
2. DAB ( Digital Audio Broadcasting )
3. ISDB-TSB ( Intergated Services Digital Broadcasting - Terrestrial Sound Broadcasting )
4. DRM ( Digital Radio Mondiale )