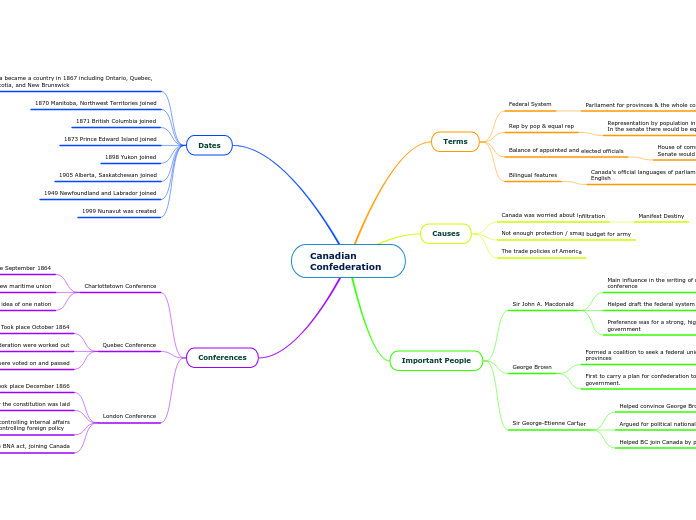
Canadian Confederation
Terms
Federal System
Parliament for provinces & the whole country
Rep by pop & equal rep
Representation by population in the house of commons
In the senate there would be equal representation
Balance of appointed and elected officials
House of commons would be elected by voters
Senate would be appointed by the Prime Minister
Bilingual features
Canada's official languages of parliament would be French and English
Causes
Canada was worried about infiltration
Manifest Destiny
Not enough protection / small budget for army
The trade policies of America
Important People
Sir John A. Macdonald
Main influence in the writing of resolutions at Quebec conference
Helped draft the federal system for Canada
Preference was for a strong, highly centralized, unitary form of government
George Brown
Formed a coalition to seek a federal union of all the British provinces
First to carry a plan for confederation to the British government.
Sir George-Etienne Cartier
Helped convince George Brown to join the great coalition
Argued for political nationality at Quebec conference
Helped BC join Canada by promising a transcontinental railway
Dates
Canada became a country in 1867 including Ontario, Quebec, Nov Scotia, and New Brunswick
1870 Manitoba, Northwest Territories joined
1871 British Columbia joined
1873 Prince Edward Island joined
1898 Yukon joined
1905 Alberta, Saskatchewan joined
1949 Newfoundland and Labrador joined
1999 Nunavut was created
Conferences
Charlottetown Conference
Took place September 1864
Original purpose was to discuss new maritime union
The Canadian delegates proposed the idea of one nation
Quebec Conference
Took place October 1864
The rules for confederation were worked out
72 resolutions were voted on and passed
London Conference
Took place December 1866
The foundation for the constitution was laid
Canada ended up controlling internal affairs
Britain ended up controlling foreign policy
Resulted in the BNA act, joining Canada