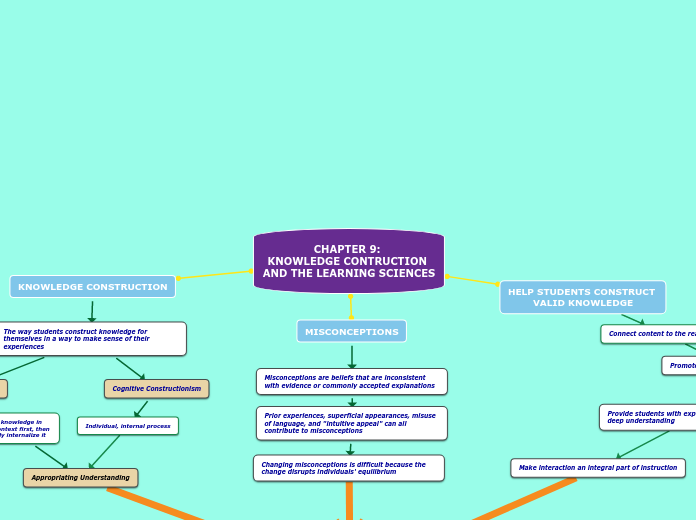
CHAPTER 9:
KNOWLEDGE CONTRUCTION AND THE LEARNING SCIENCES
KNOWLEDGE CONSTRUCTION
The way students construct knowledge for themselves in a way to make sense of their experiences
Social Constructivism
Construct knowledge in
a social context first, then
individually internalize it
Appropriating Understanding
Cognitive Constructionism
Individual, internal process
MISCONCEPTIONS
Misconceptions are beliefs that are inconsistent with evidence or commonly accepted explanations
Prior experiences, superficial appearances, misuse of language, and "intuitive appeal" can all contribute to misconceptions
Changing misconceptions is difficult because the change disrupts individuals' equilibrium