COMMUNITIES AND ECOSYSTEMS
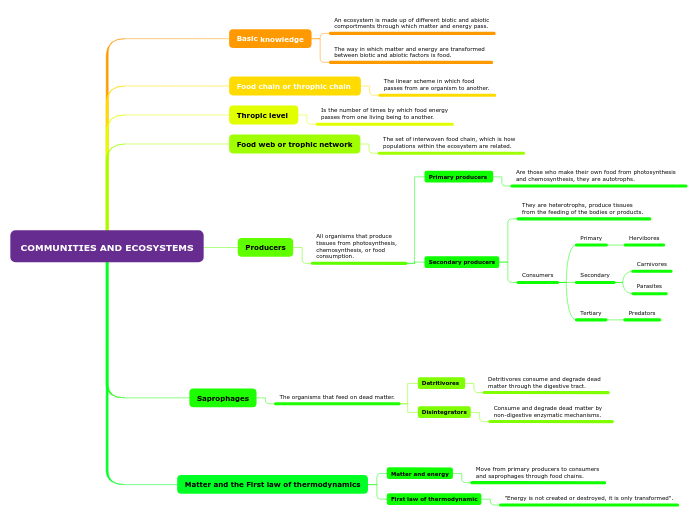
Basic knowledge
An ecosystem is made up of different biotic and abiotic comportments through which matter and energy pass.
The way in which matter and energy are transformed between biotic and abiotic factors is food.
Food chain or throphic chain
The linear scheme in which food passes from are organism to another.
Thropic level
Is the number of times by which food energy passes from one living being to another.
Food web or trophic network
The set of interwoven food chain, which is how populations within the ecosystem are related.
Producers
All organisms that produce tissues from photosynthesis, chemosynthesis, or food consumption.
Primary producers
Are those who make their own food from photosynthesis and chemosynthesis, they are autotrophs.
Secondary producers
They are heterotrophs, produce tissues from the feeding of the bodies or products.
Consumers
Primary
Hervibores
Secondary
Carnivores
Parasites
Tertiary
Predators
Saprophages
The organisms that feed on dead matter.
Detritivores
Detritivores consume and degrade dead matter through the digestive tract.
Disintegrators
Consume and degrade dead matter by non-digestive enzymatic mechanisms.
Matter and the First law of thermodynamics
Matter and energy
Move from primary producers to consumers and saprophages through food chains.
First law of thermodynamic
"Energy is not created or destroyed, it is only transformed".