Eukarya

Animalia
Porifera
Evolutionary Milestones
Simplest organism
Developed flagellated cell walls and a stomach

Xestospongia testudinaria
Cnidaria
Evolutionary Milestones
Developed Nervous System
Developed defense mechanisms
Tissues
Radial Symmetry

Aequorea forskalea
Platyhelminthes
Evolutionary Milestones
Bilateral Symmetry

Pseudobiceros gloriosus
Nematodata
Evolutionary Milestones
more advanced digestive system
Two openings allowed for greater efficiency
Developed pseudocoelom (partail cavity)

Trichuris trichiura
Annelida
Increasesd size and movememt
Segmentation
More advanced digestive system and circulatory system

Alitta virens
Mollusca
Evolutionary Milestones
More advanced circulatory and digestive system
Developed feet for better movement
Coelom (complte body cavity)

Achatina achatina
Arthropoda Evolutionary Milestones Hard exoskeleton made of chitin numerous jointed appendages and a
segmented body Developed gills or internal airways and various systems
Hexapoda-Body divided into head, thorax, abdomen uniramous appendages; one pair of antennae, Three pairs of walking legs; most with wings, Two pairs of mouthparts: mandibles and maxillae, Most possess wings as adults Undergo Metamorphosis growing from larva to adult
Insecta

Megasoma elephas
Entognatha

Allacma fusca
Chelicerata-2 body segments 6 pairs of appendages: 4 pairs for walking and 2 mouth parts
Arachnida

Latrodectus mactans
Merostromata

Limulus polyphemus
Pycgnogonida

Pycnogonida indet
Crustacea-characterized by having mandibles and compound eyes, biramous
appendages
Branchiopoda

Artemia salina
Maxillopoda
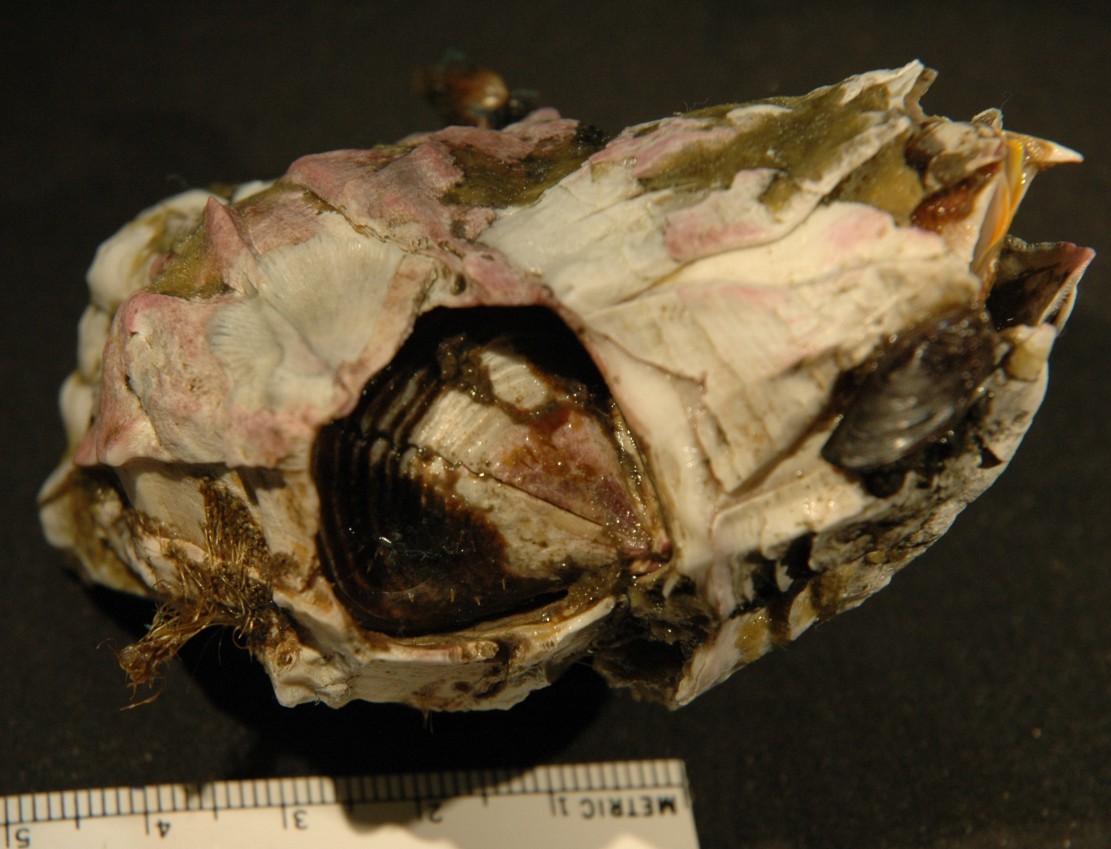
Balanus nubilus
Malacostraca

Homarus gammarus
Myriapoda-characterized by having one pair of antenna, myriads of legs and mandibles
Symphlya

Scutigerella immaculata
Pauropoda

Pauropus amicus
Diplopoda

Archispirostreptus gigas
Chilopoda

Scolopendra gigantea
Echinodermata
Evolutionary Milestones
Deuterstome
5 part Radial Symmetry
Internal Skeleton

Asterias amurensis
Chordata
Evolutionary Milestones
Notochord
pharyngeal slits
Hollow dorsal nerve chord
3 embryonic cell layers
Post-anal tail
Turnicata

Pyrosoma atlanticum
Cephalochordata

Branchiostoma lanceolatum
Vertebrata
Gnathostomata
Jawed Fish
Nostrils allowed for sense of smell
skeleton primarily made of cartilage
Skeleton formed to protect the organs within the body
exothermic
Chrondichthyes

Carcharodon carcharias
bone tissues- stronger skeleton
air bladder that performs hydrostatic functions
exothermic
Osteichcythes

Mola mola
Live on land and in water
have
young have 2 chambered hearts, adults have 3
breathe through gills lungs or skin
exothermic
Amphibia
_Edit.jpg)
Dendrobates tinctorius
adapted features for quicker movement and strong defense
Air breathing animals
Live only on the land
scales
3 chambered
exothermic
Reptilia

Python reticulatus
Have wings and feathers
Light skeletal structure
Most can fly
Endothermic
4 chambered heart-most efficient
Aves

Falco peregrinus
Have fur or hair which provides insulation and helps to keep us warm
endothermic
4 chambered heart
Have several functional internal systems which perform a variety of functions
Mammalia
Major Groupings
Only mammals which lay eggs
Reproduce sexually
Monotremes
Monotremata

Ornithorhynchus anatinus
Give early birth to a fetus which climbs from the birth canal to the mother's pouch
It is superior as the zygote has more protection as the fetus partially develops in the mothers womb before leaving the mother's womb and eggs are easier for predators to eat as they don't move. The fetus is protected in the pouch
Marsupial
Diprotodontia

Macropus rufus
Nourishment is provided for the fetus directly from its mother so that it can stay in the womb for a longer period of time until it is fully developed.
Superior to marsupials as the fetus is healthier due to the nourishment it receives. Fetus is safer as it does not leave the womb till it is mature unlike the undeveloped fetus of marsupials which leaves the womb early and climbs to the pouch.
Placental
Primates

Homo Sapien
Agnathans

Plantae
Bryophyta- non-vascular, found in fresh water environments, have rhizoids

Dawsonia superba
Gymnosperms-vascular tissue, seeds are stored inside fruit (ripened ovary) not considered real fruit, roots used to gather nutrients

Cycas revoluta
Anglosperns- produce flowers, produce seeeds enclosed in fruit, structure and adpated to gain the most sunlight exposure

Rafflesia arnoldii
Seedless Vascular- reproduce using haploid spores, do not produce flowers or seeds, have stems which provide structural support

Equisetum arvense
Protista
Plant-like
Phaeophyta
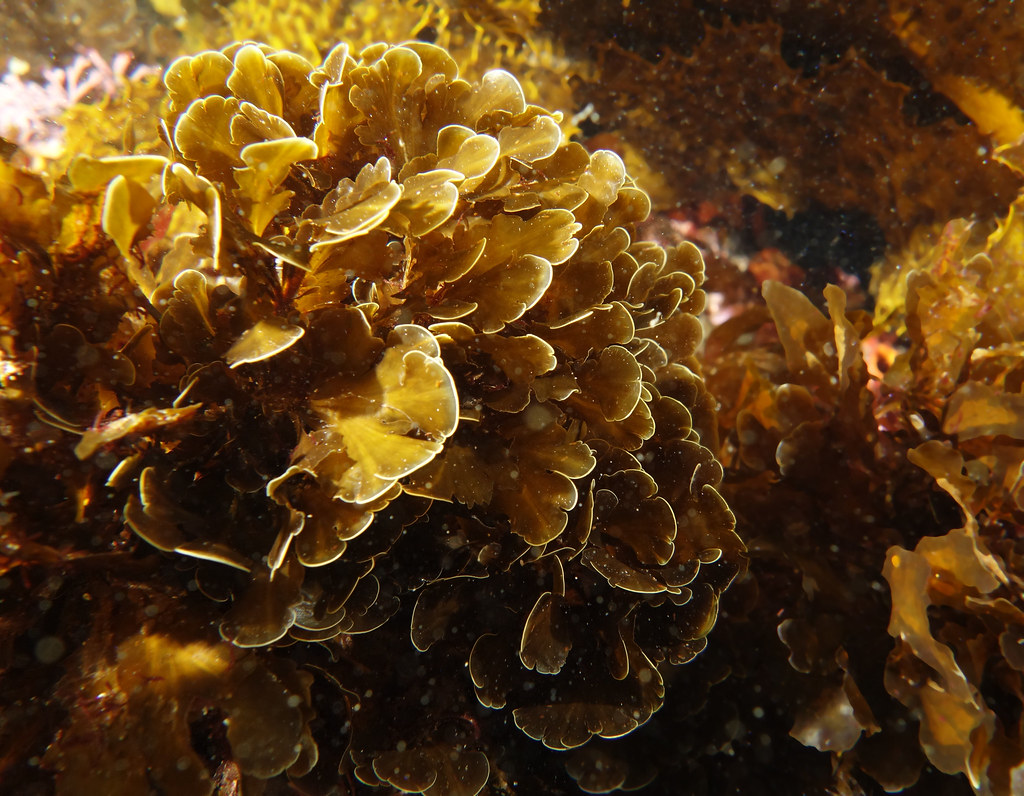

Laminaria digitata
Chlorophyta
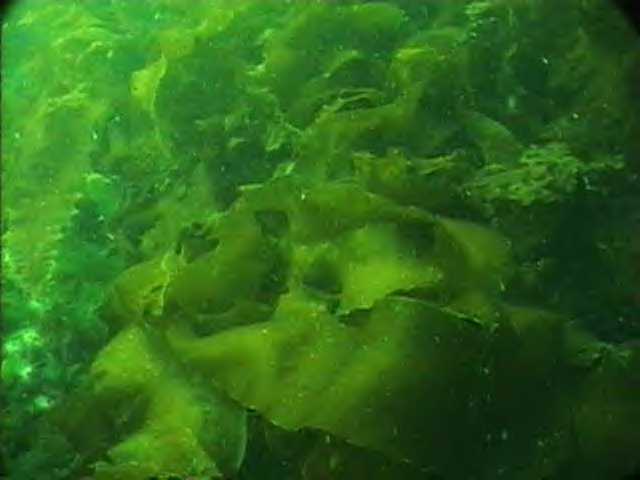

Ulva lactuca
Rhodophyta

Cyanidioschyzon merolae
Chrysophyta
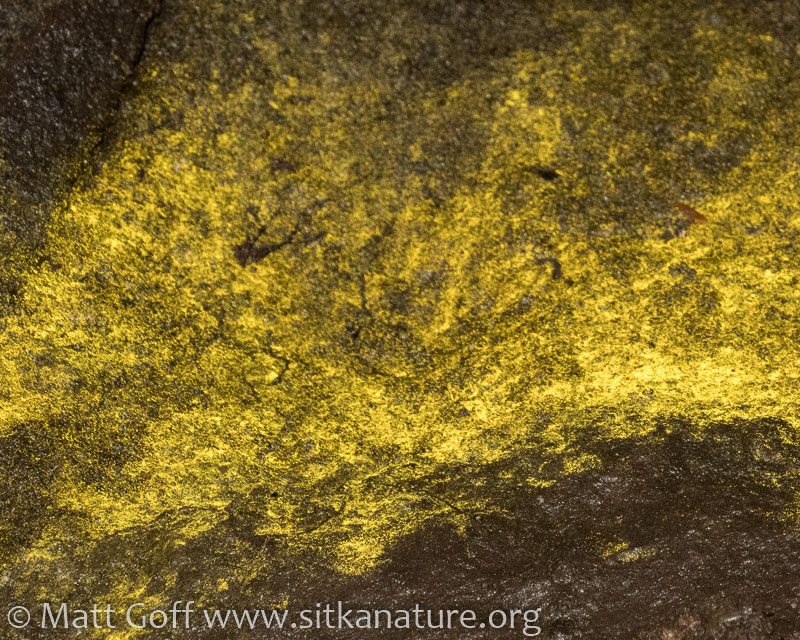

Golden Algae
Fungi-like
Acrasiomycota

Dictyostelium purpureum(Cellular Slime mold)
Apicomplexa
Plasmodium falciparum
Myxomycota

Fuligo septica (plasmodial slime mold)
Oomycota

Phytophthora infestans
Animal-like
Sarcodina
Use pseudopodia to move
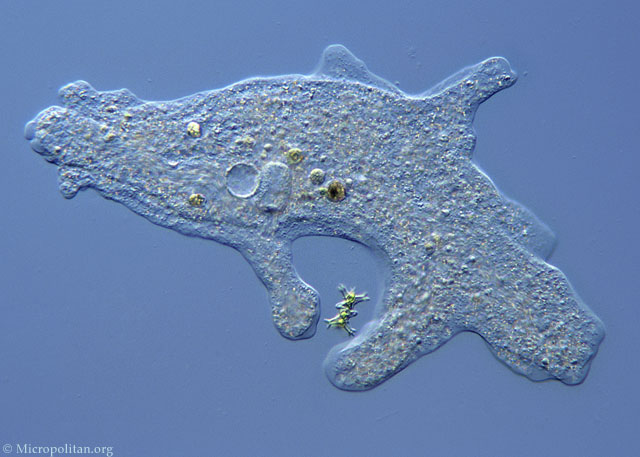
Amoeba Proteus
Ciliates
Use cilia to move

Amphorides quadrilineata
Zooflagellates
Use flagella to move

Enteromonas hominis
Sporozoans
Gliding movements

Eimeria tenella

Fungi
Zygomycota- reproduces asexually using spores called sporangiospores and sexual reproduction using zygospores

Rhizopus stolonifer
Basidiomycota- reproduce sexually and asexually. It reproduces asexually using specialized structures callled condiophores and reproduces sexually in the fruiting body

Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Ascomycota- reproduce asexually, reproduce by releasing haploid conidiophores and have sacs which contain spores
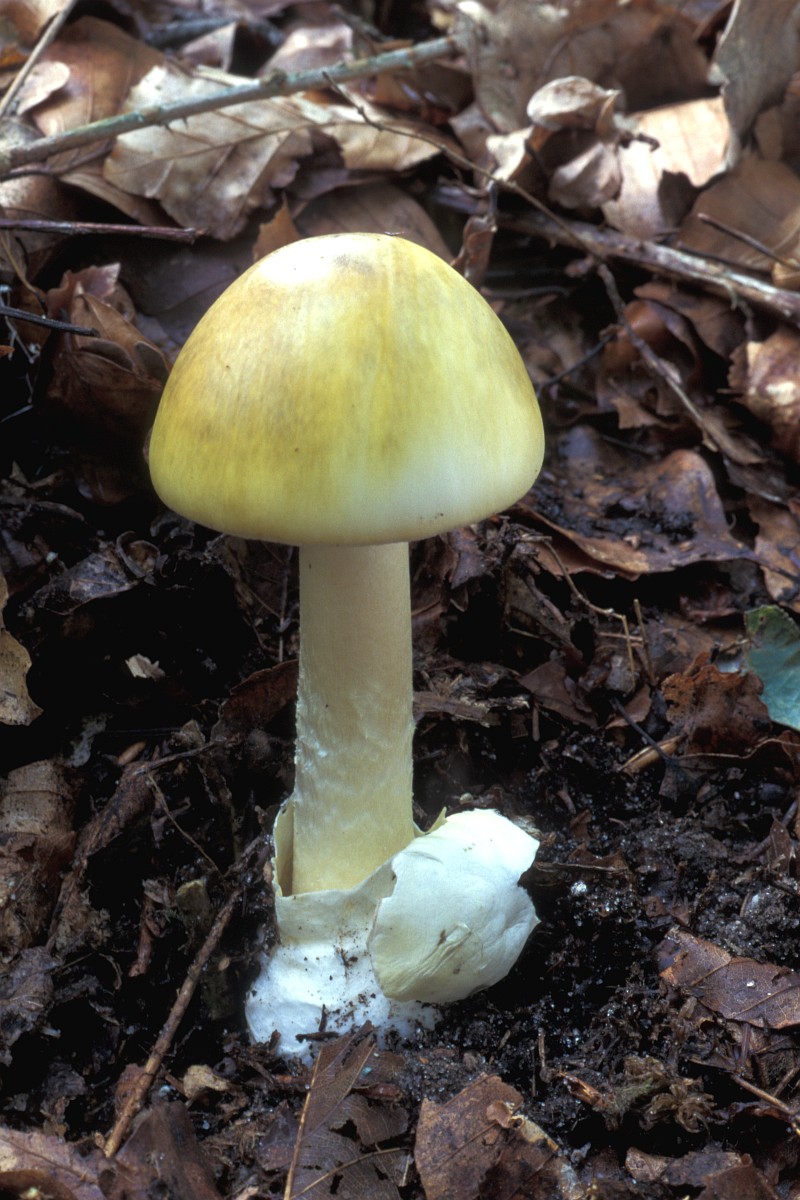

Amanita phalloides
Deuteromycota-Reproduce asexually in a process known as sporogenesis. They are known as imperfect fungi as their sexual stage of reproduction has not been oobserved
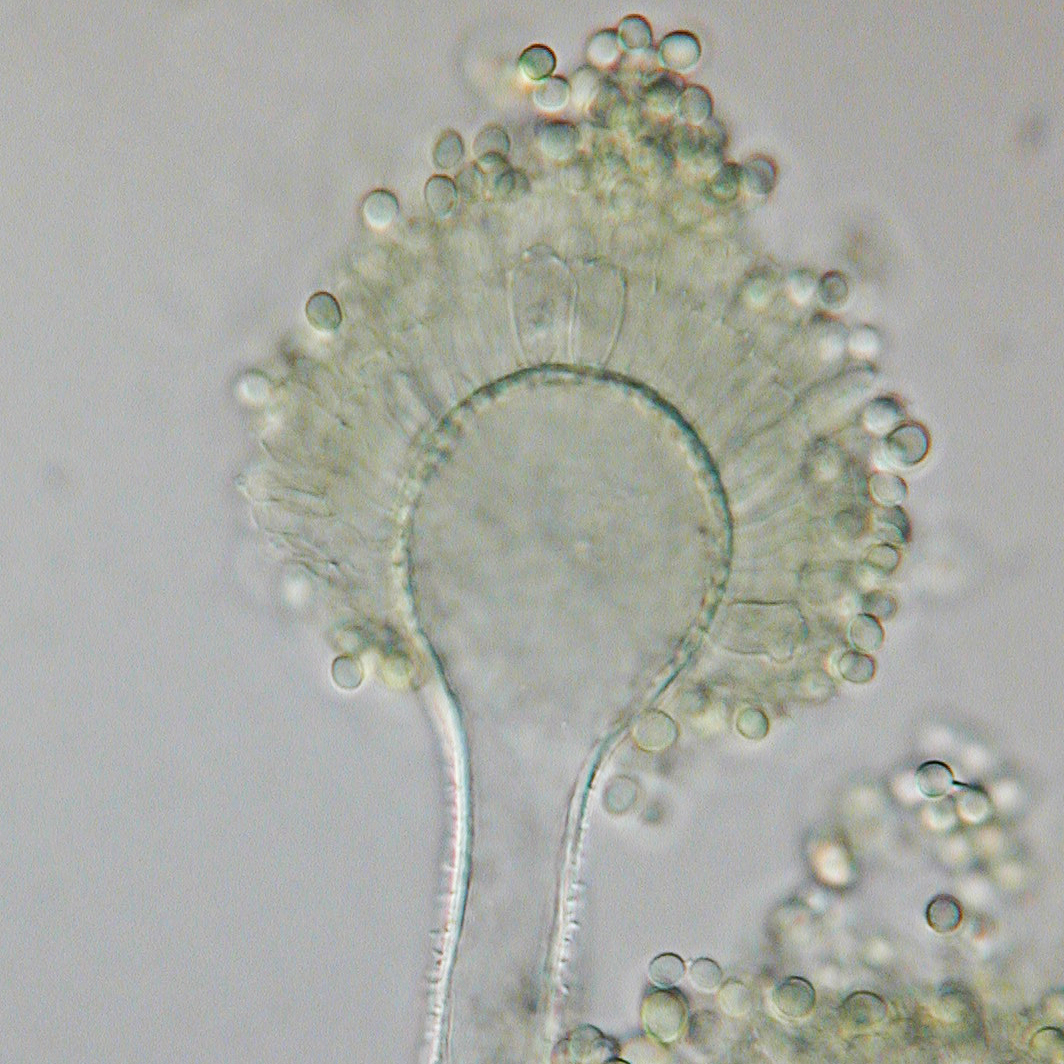
Aspergillus flavus
Archaea

Archaebacteria
Euryarchaeota
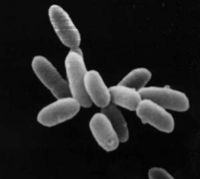
Halobacterium salinarum
Crenarchaeota

Pyrolobus fumarii
Korachaeaota

Korarchaeum cryptofilum
Bacteria

Eubacteria
Morphology
Coccus
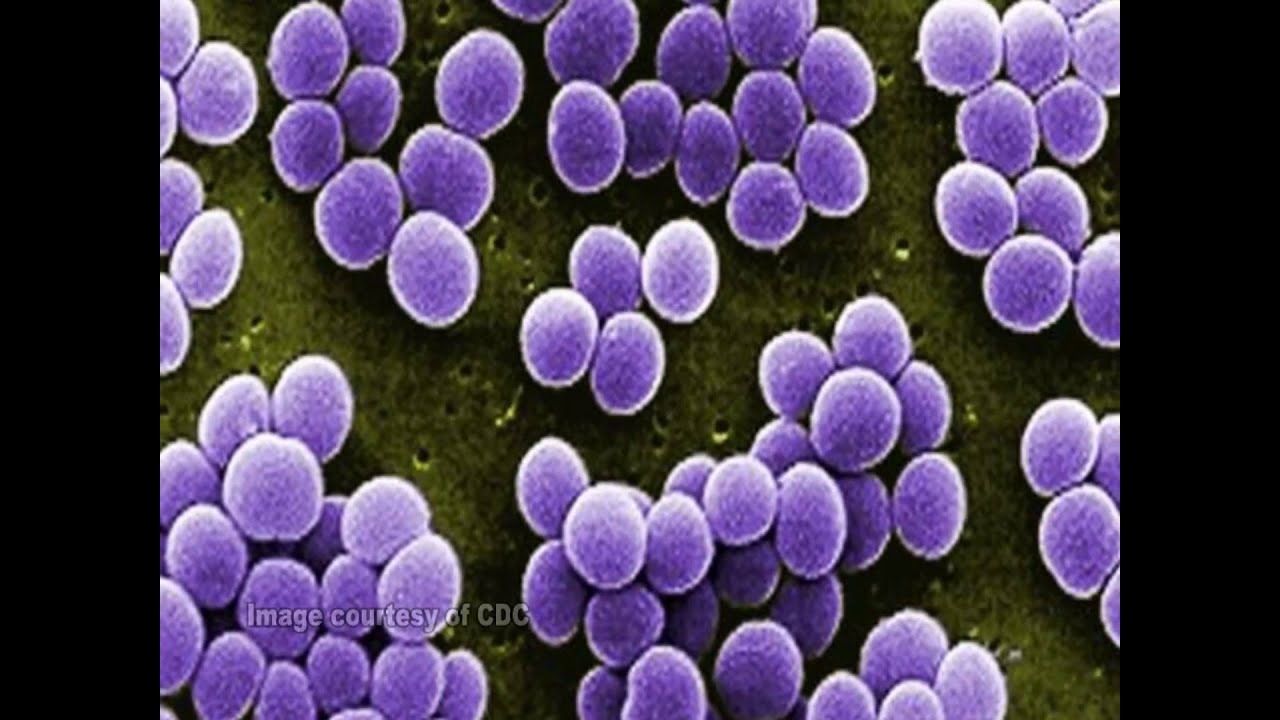
Staphylococcus aureus
Bacillus
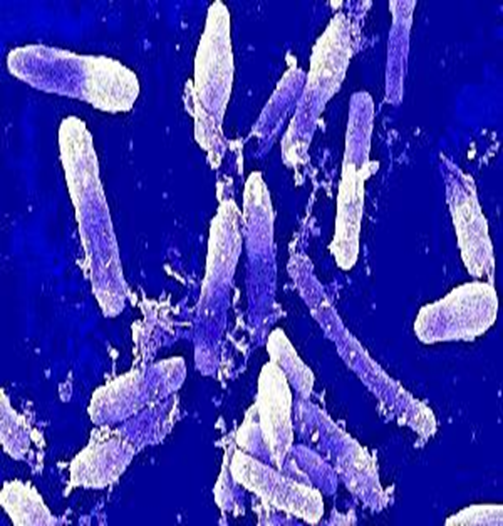
Bacillus cereus
Spiral

Spirillum volutans
membrane-bound nucleus
Reproduce by mitosis or meiosis
single-celled prokaryotic organism
survive in extreme conditions
no nucleus
no membrane bound organelles
rigid cell wall
Prokaryotes
Contains plasmids
no nucleus
single-celled prokaryotic organism
Peptidoglycan cell wall
usually reproduce by binary fission
spherical or ovoid in shape
rod-shaped
spiral-shaped
Do not photosynthesize
Eukaryotic
contain no chlorophyll
Heterotrophic
non-motile
Include methanogens which are anaerobic methane producing organisms
Include halophiles which are organimss that thrive in extremely salty environments
Includes thermophiles which are organisms that thrive in high temperatures
Include mostly thermophiles and hyperthermophiles
Found in hydrothermal environments
Oldest organisms on earth
Can survive in very high temperature, salty or acidic environments
Survive on the planets most inhospitable areas
Photosynthesize
Eukaryotic
Most are unicelleular
Cell wall made of cellulose
Cell wall made of cellulose
Multicellular
Diploid
Heterotrophic
Usually develop from a zygote(except sponges)
multicellular
Heterotrophic
Absorb nutrients
Adaptations
Complexity Increases from Porifera to Chordata
Complex Organisms
Legend
Description
Domain
Kingdom
Phyla
Subphlya
Superclass
Class
Subclass
Order