DIVERSITY MAP
Eukarya
Animalia
Evolutionary Milestones
-Very simple organism
-Formed a stomach and flagellated cells to create the flow of water
Porifera

Demospongiae
-Formed a nervous system
-Created various modes of defense
Cnidaria

Anthozoa
-Segmented parts
Platyhelminthes

Cestoda
-Formed a more advanced digestive
system
-More efficient (2 openings)
Nematoda

Secernentea
-Has a coelom to protect vital body organ systems
-Developed both circulatory system & digestive system
Annelida

Polychaeta
-Features a mantle
-Has feet for quicker and easier movement
-Developed a more advanced digestive and circulatory system
Mollusca

Octopoda
-Has jointed legs
-Exoskeleton made out of chitin
-Developed gills or internal airways with jointed appendages
Arthropoda
Myriapoda
Symphyla

Hanseniella
Diplopoda
Macroxenodes bartschi
Chilopoda

Scutigeromorpha
Pauropoda

Lestes sponsa
Crustacea
Branchilopoda
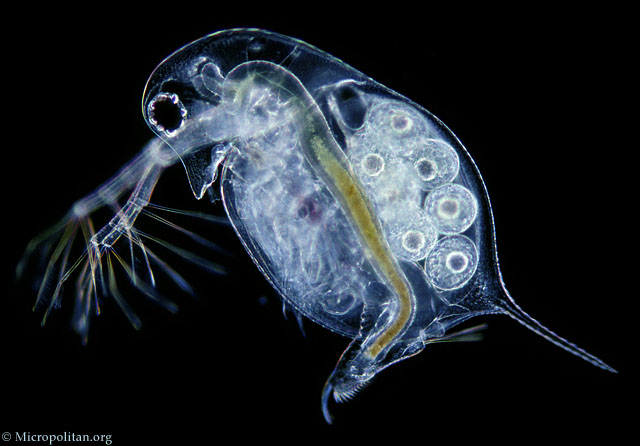
Cladocera
Malacostracans

Brachyura
Ostracoda

Podocopida
Maxillopoda

Mystacocarida
Chelicerates
Merostomata

Limulidae
Pycnogonida

Nymphon
Arachnida

Buthidae
Hexapoda
Entognatha

Collembola
Insecta

Formicidae
-Radial symmetry
-No head
-Has nerves that circle from the mouth and extend to its arms
Echinodermata
Asteroidea
-Formed a backbone
-Most complex organ and organs systems
Chordata
Cephalochordates
Tunicates
Vertebrate
Agnathans
Gnathostomata
Adaptations to Terrestrial Life
-Jawed fish
-Nostrils allow sense
of smell
-Hard skeletons which
start to form to protect
the organs of the body
Chondrichthyes
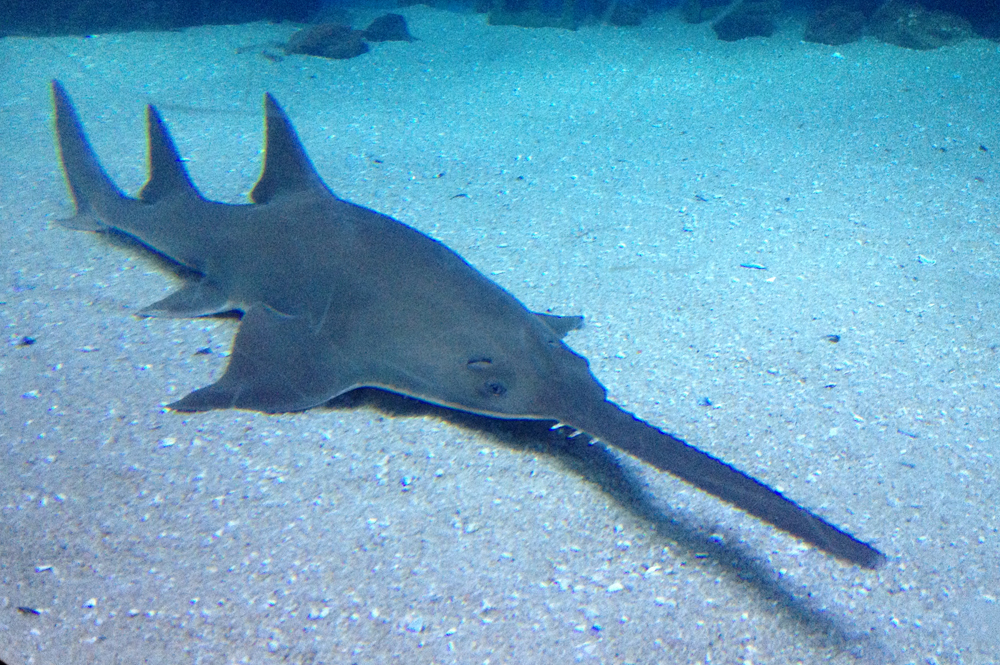
Pristidae
-Live in water and land
-Form both gills and lungs
Amphibia

Dendrobatidae
-Air breathing vertebrates
-Live only on land
-Have developed modes for
quicker movement and strong
defense
Reptilia

Crocodylus acutus
-Have feathers instead of hair
-Learned to fly
Aves

Agapornis
-Have fur/hair which allows for insulation
-Adapted to have full working internal
systems and different modes of nutrition
Mammalia
Major Groupings
-Only living mammals
where females lay eggs
-Reproduce sexually
-Solitary animals during
mating season
Monotremes

Ornithorhynchidae
-Give early birth to a
fetus which climbs from
mothers birth canal
-Superior to monotremes
because there is more
protection for the zygote
Marsupials

Vombatidae
-Substances are passed from the
mother to the fetus in order for
it to stay longer in the womb until
mature
-Superior to marsupials as zygotes
are healthier due to placenta
-Also have ability to get away from
prey quicker so zygote does not die
Placentals

Homo Sapiens
Protists
Protist groups
Plant-like
Pyrrophyta

Dinophyceae
Chrysophyta
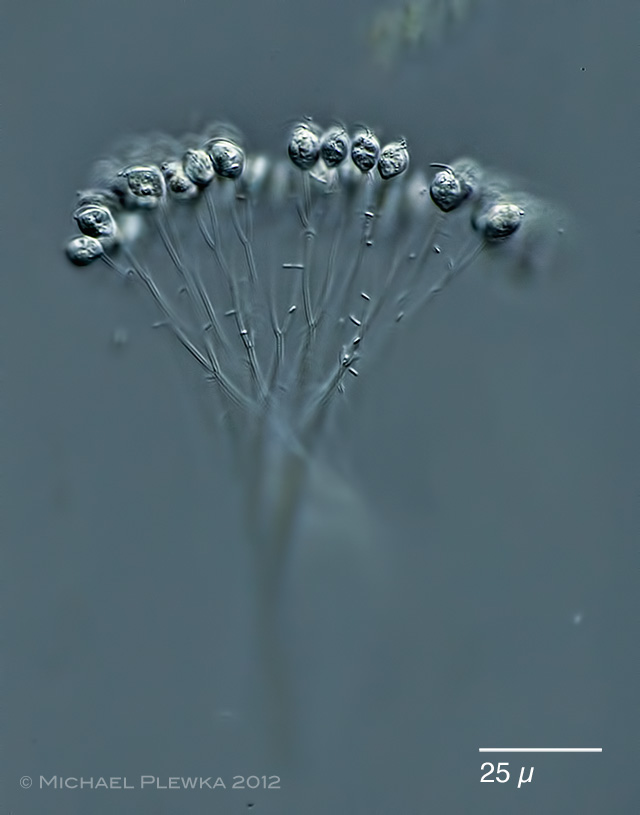
Ochromonadales
Phaeophyta

Laminariales
Rhodophyta

Corallinales
Euglenophyta

Chlamydomonas nivalis
Chlorophyta
Prasinophyceae
Animal- like
Sporozoans
Sarcodina
Zooflagellates
Ciliates
Fungi- like
Myxomycota

Dictyosteliomycetes
Chytridiomycota

Allomyces
Oomycota

Phytophthora
Dictyostelid

Dictyostelium
discoldeum
Plantea
Bryophyta
Seedless Vascular
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Fungi
Reproductive Structure/Strategies
-Sexual Reproduction
-Reproduce through
fruiting club fungi
Basidiomycota

Agaricomycetes
-Uses both asexual reproduction
and sexual reproduction
-Sexual reproduction occurs only when conditions
are unfavorable and cannot reproduce asexually
-Asexual reproduction happens through the use of spores
-Sexual is through the use of conjugation
Zygomycota

Kickxellomycotina
-Asexual reproduction
-"Imperfect Fungi"
Deuteromycota
Hyphomycetes
-Asexual reproduction
-Reproduce through
releasing haploid
conidiophores
-Have sacs for spores
Ascomycota

Pezizomycotina
Bacteria
Eubacteria
Morphology
Bacillus

Lactobacillus plantarum
Spirillum

Spirillum winogradskyii
Coccus

Staphylococcus aureus
Archaea
Archaeabacteria

Thaumarchaeota
Euryarchaeota

Crenarchaeota
Rigid cell wall
Able to survive harsh conditions
Single-cell prokaryotic organisms
No membrane bound organelles
No Nucleus is present
Oldest organisms on earth
Ability to live in hot, acidic and salty environmental conditions
Can be found in the harshest regions on earth
Unicellular
Plasmid
Prokaryotes
Nucleus is present
Single- cell prokaryotic organisms
No Nucleus is present
Reproduces by either mitosis or meiosis
Contains all complex organisms
Membrane-bound
Several chemical types of cell walls
Coccidiasina

Hexamita

Spirotrichea
Difflugia

Leucobryum glaucum

Pteridium aquilinum

Ginkgo biloba
Dicotyledon
Eukaryotic
Small and visible under a light microscope
Forms of movement:
Psudopod
Cilia
Flagella
Utilizes photosynthesis
Holozoic
Saprozic
Absorbs nutrients
Heterotrophic
Develops from a zygote
Multi cellular
Diploid
Can perform photosynthesis
Cell wall made of cellulose
Multicellular
Multi-cellular or unicellular
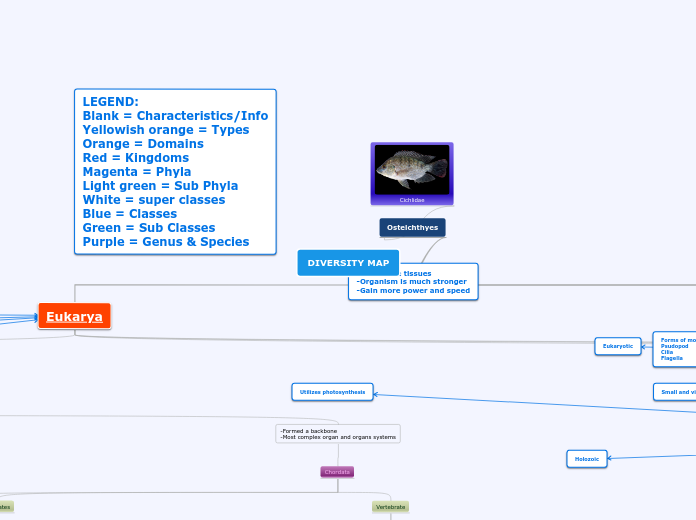
-Have bone tissues
-Organism is much stronger
-Gain more power and speed
Osteichthyes

Cichlidae