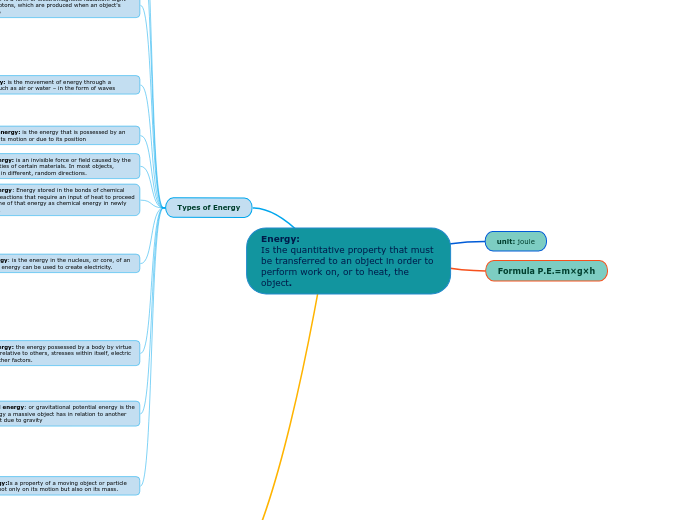
Energy: Is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object.
unit: joule
Formula P.E.=m×g×h
Types of Energy
Heat Energy: Heat is the form of energy that is transferred between systems or objects with different temperatures.
EXAMPLE: The sun. UNIT: calorie and kilo calorie. FORMULA: The equation for calculating heat energy is q=mCpΔT, where q is the heat variable, m is the mass of the object,Cp is the specific heat constant and ΔT is the temperature change
Electrical energy: Electrical energy is a type of kinetic energy caused by moving electric charges.
UNIT: Watts and Kilowatts. FORMULA: Electrical energy=Power x Time. EXAMPLE: Washing machine, and dryer
Light energy: is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light consists of photons, which are produced when an object's atoms heat up
UNIT: ELECTRON-VOLTS(eV)
FORMULA: E = h f where:
E = Energy of the photon (in Joules)
h = Constant, actually known as Planck's constant, a really ugly number
f = frequency of the light in units of per seconds (1/seconds)
EXAMPLE: Lightened candle, fire, flashlight and electric bulb
Sound energy: is the movement of energy through a substance – such as air or water – in the form of waves
FORMULA:I = Δ p 2/ 2 ρ v w. Δ p Change in pressure, or amplitude p- density of the material the sound sound is travelling through vw - speed of observed sound.
UNITS : 1 Joules per cubic meter(J/m3)
EXAMPLE: Balloon and popping horn
Mechanical energy: is the energy that is possessed by an object due to its motion or due to its position
formula : mechanical energy = kinetic+ potential energy. UNIT: Newton Meter. EXAMPLE: Hammer, dart gun and wind mill.
Magnetic energy: is an invisible force or field caused by the unique properties of certain materials. In most objects, electrons spin in different, random directions.
EXAMPLE: The Generator. FOMULA: E=1/2 LI2. UNIT: Teslas
Chemical energy: Energy stored in the bonds of chemical compounds. Reactions that require an input of heat to proceed may store some of that energy as chemical energy in newly formed bonds.
EXAMPLE: The coals and woods. UNIT: Jouls. FORMULA: K.E. = \frac{1}{2} \times m \times v^2.
Nuclear energy: is the energy in the nucleus, or core, of an atom. Nuclear energy can be used to create electricity.
formula: E = mc2 explains this. The equation says: E [energy] equals m [mass] times c2 [c stands for the speed or velocity of light].
UNIT: The mass defect of about 0.2 atomic mass units is converted into an energy of 210 MeV For an atomic mass unit, u, we have u ≈ 1.66 × 10−27 kg, and the atomic energy unit electron volt, eV, is about 1.60 × 10−19J
EXAMPLE: The sun
Potential energy: the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position relative to others, stresses within itself, electric charge, and other factors.
FORMULA: U=m g h
U = gravitational energy
m = mass
g = gravitational field
h = height
UNIT: (Kgxm2s2)
EXAMPLE: Water that is behind a dam
Gravitational energy: or gravitational potential energy is the potential energy a massive object has in relation to another massive object due to gravity
FORMULA: PEg=mgh. EXAMPLE: A car that is parked at the top of the hill. UNIT: Newtons per kilogram (N/Kg)
Kinetic energy:Is a property of a moving object or particle and depends not only on its motion but also on its mass.
VIBRATIONAL KINECTIC ENERGY: Is the kinetic energy an object has due to its vibrational motion.
TRANSATIONAL KINETIC ENERGY: A body is equal to one-half of the product of its mass,m and the square of its velocity.
ROTATIONAL KINECTIC ENERGY: Is the kinectic energy due to the rotational of an object and is the part of its total kinectic energy
EXAMPLE: Moving car, Bullet from the gun, Flying Airplane. Formula: K.E=1/2m v2. UNIT: 1kg m2/s2.
LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY: The law of the conservation of energy states that the energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Only converted from one form of energy to another.
Applications: (1) when the pendulum swings upwards, the kinetic energy is converted to potential energy. (2) When the water falls from the sky, It converts potentials energy to kinetic energy.