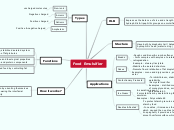
Food Emulsifier
HLB
Expresses the balance of size and strength of the hydrophillic & lipophillic groups on emulsifier
High HLB ( >10 ) Relatively more polar ( hydrophillic ) , Good w/o emulsifier
Medium HLB ( 7-9 ) - Good wetting agent , can be used in both o/w & w/o emusulsifier
Low HLB ( 3-6 ) - a good o/w emulsifier
Stucture
Have both hydrophobic tail ( hates water ) and hydrophillic head ( water loving )
Applications
Breads
-Dough conditioner & crumb softener
- Form complex with amylose to retard starh retrogradation
Example : stearoyl lactylate
Cakes
-Stabilize the aerated structure
-Promote finer distribution of fat droplets
Examples : mono and diglycerides , propylene glycol ester
Confectionary Products
-To inhibit bloom, stabilize gloss and improve palatibility
-As crystal modifier
Examples : distilled monoglycerides, lactic acid ester of monoglycerides, sorbitan mostearate and polysorbate 60
Ice Cream
-As aerating agent
-Form stabiliser by destabilizing the product's emulsion
Examples : Polysorbate 65
Noodles & Pastas
-To protect starch granules and improve quality of starchy food
- In noodles, it increases the water absorption rate which caused the noodles to become less sticky
-In spaghetti, it provides a feeling of elasticity and smooth uniform surface which inhibi
Types
Non-ionic
uncharged molecules
Anionic
Negative charged
Cationic
Positive charged
Amphoteric
Positive & negative harged
Functions
To stabilize the emulsion, stabilized aerated system and control agglomeration of fat globules
To modify texture,shelf life and rheological properties by complexing with starch and protein components
Improve texture of fat-based food by controlling fat polymorphism
How it works?
Reducing the surface tension by orienting themselves at the phase interface and lowering the interfacial energy that leads to instability