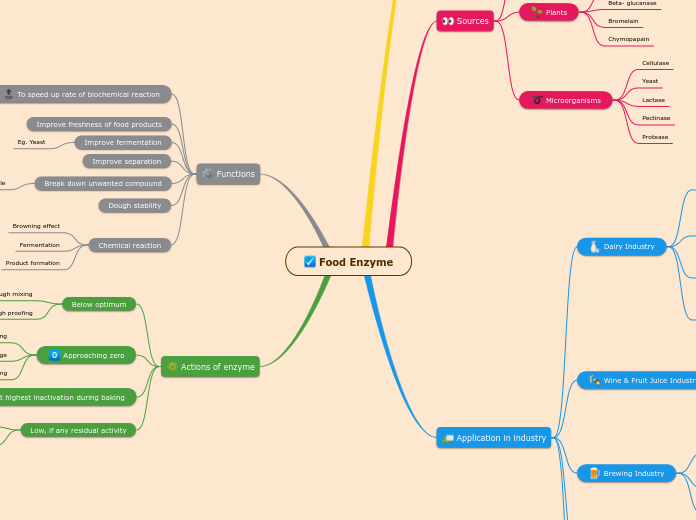
Food Enzyme
Definition
A specialized protein which acts as a catalyst in living organism
Has a 3-dimensional structure with globular shape
Enzyme-substrate complex is formed
to convert reactant into product
Sources
Animals
Catalase
Rennin
Amylase
Lipase
Plants
Alpha-amylase
Beta- glucanase
Bromelain
Chymopapain
Microorganisms
Cellulase
Yeast
Lactase
Pectinase
Protease
Application in industry
Dairy Industry
Protease:
Form a bitter taste in cheese
Hydrolyze specific peptide bond to form para kappa casein & macro peptide in cheese
Catalase:
To preserve natural milk enzyme when making cheese
To develop flavour in cheese
Rennet:
Separate solid curd and liquid whey to produce cheese
Milk coagulation
Lipase:
Hydrolyse milk fat and give flavours to cheese
Decrease ripening time of cheese
Wine & Fruit Juice Industry
Carbohydrase:
Improve juice colour & aroma
Beta-glucanase:
Reduce maturation period increase juice production
Acid protease:
Decrease protein in juice & concentrate
Pectinase:
Extraction of colour & juice from fruit
prevent pectin from forming haze
Brewing Industry
Alpha-amylase:
Starch --> dextrin in corn syrup production
Reduce mashing time in brewing
Protease:
Break down larger molecules of protein enhance heat retention of beer reduce haze
Beta-glucanase:
Break down glycosidic bonds in beta-glucan aid in filtration after brewing and mashing
Meat Industry
Protease
Loosen the muscle fibre by hydrolyse the bond that holds amino acid together
Transglutaminase
Gelation in meat product
Actinidin
To enhance tenderness in processed meat
Baking Industry
Alpha-amylase
Produce dextrin which will be further broken down to sugar
Lipoxygenase
To whiten bread
Hemicellulase
To decrease stickiness of bread
Protease
To reduce gluten elasticity
Beta-amylase
Improve fermentation of yeast
Enhance bread volume
Functions
To speed up rate of biochemical reaction
Shorter mixing/ proofing time
Without decrease the quality of products
Improve freshness of food products
Improve fermentation
Eg. Yeast
Improve separation
Break down unwanted compound
Example
Break down the pentosans in rye and whey flour which delay the development of gluten
Dough stability
Chemical reaction
Browning effect
Fermentation
Product formation
Actions of enzyme
Below optimum
Dough mixing
Dough proofing
Approaching zero
Freezing
Frozen Storage
Thawing
At highest inactivation during baking
Baking
Low, if any residual activity
Cooling
Bread storage