
Interactions in the physical environment
Earthquakes
Caused by shift of tectonic plates
When the plates get Slid past each other and grind causing an earthquake
When the plates separate and create new land causing earthquake
When the plates hit together and one gets pushed down. then eventually gets shot back up causing earthquake
Are We Ready
We are not ready
Many of Our buildings and structures would be destroyed if a large enough earthquake hit us.
Tectonic Plates
20 on earth
move by convection currents
(magma under plates moving)
2 Types - Oceanic and Continental
Range from 20 km thick (pacific) to 100 km thick (eurasian)
plate tectonics helped shape the earth
ex. large plates: north american small plates cocos plate
mainly continental crust: Eurasia, mainly oceanic crust: pacific
Boundaries of Plates
Subduction Zone
Plates converge and One Plate Dives Under the Leading Edge of its Neighbour
Ridge Axis
Plates are diverging and new ocean floor is generated
Transform
Plates Slide Past Eachother
Continental Drift
The Theory Discovered by John Tuzo Wilson That all Continents were once attached as one Super Continent (Pangaea) and drifted into separate positions Later.
4 Proofs
Jigsaw Fit
Continents Fit Together Like Puzzle
Fossils
Same Land Animals & Plants in South America & South Africa
Mountains
Same Age & Structure of Mountains in Eastern Canada (Appalachians) & Western Europe (Caledonians)
Ice
Evidence of Past Glaciers in Warm Places Today. Which Means Continents Used to be Closer to the Poles
Geologic History
The 4 Eras
Precambrian Era
Changes to Land
1. New Mountains Formed
2. New Land and Oceans
3. Contains Mostly Igneous and Metamorphic Rock. Some Sedimentary
Living Things
Fossils, Algae, Some More Complexed Organisms
4.6 billion yes ago
lasted 4 billion yrs (87% of time)
Paleozoic Era
Changes to Land
1. Collision of Pangaea Caused Eastern Part of North America to Crumble and fold to Create Appalachian Mountains
Living Things
Shell's , Other Simple Things, More Advanced Things, Plants, Trees, Fish, Insects, Amphibians
570 Million Yrs Ago
Lasted 325 million Yrs (7% of time)
Mesozoic Era
Changes to Land
1. North American Plate Collided with Pacific Plate
Caused Magma to Raise to Top of North American Plate
Cooled to Granite
Formed Coast Range Mountains
2. Earth Folds Forming Rocky Mountains
Caused By Tectonic Forces
Appalachians eroded
Living Things
Plants, dinosaurs, Birds, Small Sea Creatures
245 Million Yes Ago
Lasted 180 Million Yrs (4% of time)
Cenozoic Era
Changes to Land
1. Coast Mountains Uplifted
2. Rockies Formed by Folding, Faulting, Volcanos
3. glaciers scrap and gouge land
4. Appalachians and Canadian Shield Rounded
Caused by erosion
Living Things
Mammals, fish, and Plants
65 Million Yrs Ago
Hasn't Ended Yet (2% of time, so far)
Glaciation
How Do Glaciers Form?
Snow Accumulates-Hundreds of Metres Thick
Weight of Snow Causes Bottom Layers to Turn to Ice
How is Glacial Ice Different From Regular Ice?
It is Formed Differently
It is Denser
It is Less Polluted (Because it Was Formed a Long Time Ago
How do Glaciers Move?
a. Alpine Glaciers
Move Down Valleys From High Elevations to Low Elevations Due to Gravity
Move a Few Centimetres Per Day
b. Continental Glaciers
Move Under Their Own Weight
Spread Outward From the Centre
When do Glaciers Change Size?
Become Larger When the Rate of Accumulation > Melt (Advancing)
Become Smaller When the Rate of Melt > Accumulation (Retreating)
How do Glaciers Change Landforms?
Press Down on Land - Now Rebounding About 1-2 Cm Per Century
Alpine Glaciers Sharpen Upper Portion of Mountains (Give Them a Rugged Appearance) and Create Broad U-Shaped Valleys
Continental Glaciers Smooth out the Land by Eroding High Points and Filling in Low Points
What Force Turns Fallen Snow to Ice
Compacting
Landform Region
7 Regions in Canada
Western Cordillera
Formed by
North American Plate Collision With Pacific Plate
Landforms
Coast Mountains, Interior Plateau, eastern mountains
Mostly Sedimentary
Human Activities
Farming, Mining, Whale Watching, Tourism
Descriptive Words
Glaciers, Inlet (Narrow area of water)
Canadian Shield
Formed by
Magma and Molten Rock Rose to Surface as Volcano
Landforms
Rounded Hills of Rock
Rock Type
Metamorphic
Human Activities
Mining, Farming, Fishing, Camping
Descriptive Words
Nature
Appalachian Mountains
Formed by
Layers of Sedimentary Rock Uplifting and Folding After North American Plate Collided with European and North African Plate
Landforms
Rounded, Large Hills, Long Bays, Deep Harbors, Many Wide Valleys
Rock Type
Sedimentary
Human Activities
Boating, Fishing, Farming
Descriptive Words
Eroded (Slowly Damaged Rock or Land
Innuitian Mountains
Formed by
North American Plate Moving Forward
Landforms
Mountainous Measuring 2500 M, Bumpy, Barren (No Trees/Vegetation) - Because its to Cold
Rock Type
Sedimentary
Human Activities
Remote (No Human Activity)
Descriptive Words
Snowy, Icy, Extremely Cold
Interior Plains
Formed By
Rocks under Canadian shield getting damaged
Landforms
Flat, Rolling Hills, Wide River Valleys
Rock Type
Sedimentary
Human Activity
Farming, Transportation, Fishing, Boating, Hiking, Skiing
Descriptive Words
Flat
Great Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands
Formed by
erosion from Canadian shield bringing in sediments to the area. and glaciers carried sand, gravel, soil to the area
Landforms
Rolling Hills, Flat Plains, Deep River Valleys
Rock Type
Sedimentary
Human Activities
Farming, 50% of Canada's Population Lives Here
Descriptive Words
Flat Land, Rivers
Hudson Bay - Artic Lowlands
Formed by
Sand, Silt, and Clay Which Came at The End of The Ice Age and Formed Rock Which Created The Land
Landforms
Low, Swampy, Forest, Rolling Landscape
Rock Type
Sedimentary
Human Activities
Mining
Descriptive Words
Lots of Forest, Swampy
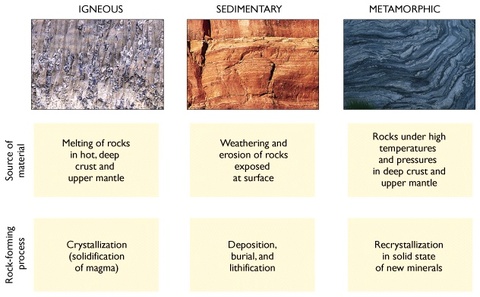
Rock Cycle
Rock Types
Sedimentary
Formed from - sand, shells, other fragments of material
Can see - sand, pebbles, and stones. Contains fossils
Ex. conglomerate and limestone
Metamorphic
Formed from - heat and pressure underground
Can see - Ribbon like layers. May have shiny crystals
Ex. gneiss and marble
Igneous
Formed from - Magma cooling and hardening
Can see - Tiny holes/spaces, gas bubbles, glasslike surface
Ex. basalt and obsidian

Heat and Pressure
Cooling
Compacting and Cementing
Lateral Moraine
Ice floe
Grooves in rocks made by passing glaciers
Erratic
Sediment
A cave Formed by ice when glacial ice melts
Magma
Weathering and Erosion

Ice Cave
Oval shaped hill made from glacial deposits. Looks like half an egg laid on a flat surface, from the side
Heat and Pressure
Weathering and Erosion
Rock Cycle
Sedimentary Rock
Melting
A mounded glacial deposit at the bottom of the side of a valley
Melting

Ice Shelf
A large boulder that was picked up by a glacier and moved away from original area
Striations
A large sheet of free floating ice, usually flat on its top side

Igneous Rock
Terminal Moraine
A large sheet or shelf of ice that extends into an ocean. Shelf is attached to land or glacier
Metamorphic Rock

