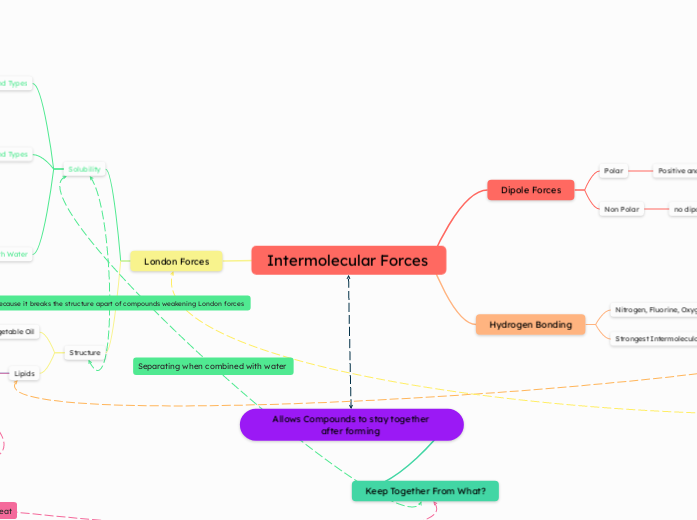
Intermolecular Forces
Dipole Forces
Polar
Positive and Negative Dipoles
Attract to surrounding dipoles of other molecules
Strength Also depends on polarity of the molecule
Similar Mass and Size
Increases Dipole Forces Strength
Different mass and size
Weakens Dipole Forces Strength
Non Polar
no dipoles
Therefore no Dipole Forces
Hydrogen Bonding
Nitrogen, Fluorine, Oxygen
Mustard Powder
Carbohydrates, Proteins. (Hydrophilic)
Reacts with Vinegar. (Basically Water)
Creates Hydrogen Bonding
Stabilizes mixture of oil and vinegar
Creates Salad Dressing
Lipids, and Oils (Hydrophobic)
Reacts with the Oil
Creates London Forces
Strongest Intermolecular Force
London Forces
Solubility
Two Different Bond Types
Insoluble With One Another
Two Same Bond Types
Soluble With Each other
With Water
Hydrophobic Compound's
Insoluble with water
Nonpolar bonds
Polar and Ionic Bonds
Hydrophilic Compound's
Soluble with water
Structure
Vegetable Oil
Double Bond
Add Water Getting Rid of Double Bond
Structure Tightens
Hydrated Vegetable Oil
Lipids
Unsaturated Fats
Makes Weaker London Forces due to structure being further apart
Which makes Weaker Intermolecular Forces
Saturated Fats
Makes Stronger London Forces
Which Makes Stronger Intermolecular Forces
Melting/Boiling Point
Low
Will melt at room tempature
High
Will not melt at room tempature