Maahi's Chemistry Connections
Measurement and Data Processing
Lab Equipment
Graphing Techniques

Significant Figures: the number of digits reflecting the precision of a given measurement
Scientific Notation: used to make numbers and quantities easier to comprehend and write
Precision
Random Errors: Uncontrolled variables in an experiment
Accuracy
Systematic Errors: Flaw in the actual experimental design, defect with instrument or the way the measurement was taken
Stoichiometry Relationships
Mole Concept
Mole (mol)
n=N/L
n=m/M
Molar Mass (g/mol)
M=m/n
Avogadro's Constant 6.02×10²³ objects/mol⁻¹
Limiting Reactant: the first reactant to be consumed completely in a chemical reaction
Excess Reactant: the reactant that could keep reacting if limiting reactant had not been done
Titrations: technique where solutions of known concentration is used to determine concentration of unknown solution (n=CV)

Isotopes: atoms of the same element with different mass numbers, but similar chemical properties
Mass spectrometer
Atomic Structure
Electron Configuration
Ionization energy: minimum energy required to remove an electron from a neutral gaseous atom/moleule in its ground state
x^(n-1)(g) → x^n+(g) + e⁻
Orbital
Hund's Rule: orbitals of same sublevel are filled singly, then paired up
Aufbau Principle: electrons are added to lowest energy level first
Pauli Exclusion Principle: no more than two electrons per orbital and they must spin oppositely

Each orbital has a specific energy level, with 1s being the lowest energy level
Standard Notation

Periodicity
Periodic Trends
Ionization Energy/ Electron Affinity
Decreases down a group/ Increases across a period
Atomic Radius
Increases down a group/ Decreases across a period
Electronegativity
Decreases down a group/ Increases across a period
Melting and Boiling Point
Decreases down a group/ Increases across a period until group 14 and then decreases
Metals
lose electrons in reactions (cations)
Non-Metals
gain electrons in reactions (anions)
Chemical Bonding and Structure
Hybridization
formed when two atomic orbitals, each containing one electron, overlap to from a new combined orbital
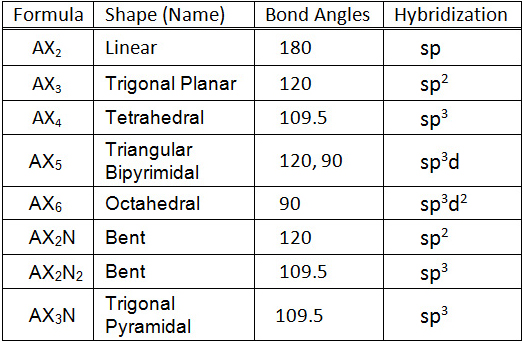
Vespr Theory: used to predict 3D molecular geometry based on the atoms/ions valence shell electron bond pairs
Molecular Polarity
Intermolecular Forces
forces that exist between molecules
London Dispersion Forces → all molecules(polar/nonpolar)
Dipole-Dipole/Hydrogen Bonding → polar
partial charge distribution of atoms in a compound is uneven which is dependent on individual molecular geometry and symmetry
Ionic Bonding
metals and nonmetals (ΔEN ≥ 1.8)
Covalent Structures
nonmetals (0 ≤ ΔEN ≥ 1.7)
Bond Length
measure of the distance between two bonded nuclei
Bond Strength
measure of energy required to break bond
Thermochemistry
Standard Enthalpy Change
Neutralization
enthalpy change when a strong acid and base react together to form one mole of water under standard conditions
1. Calculate the number of moles of acid and base using n=cv
2. Determine the limiting reactant
3. Add the volumes of acid and base together (where 1cm^3=1g) to get the mass
4. Use Q=mc∆T to calculate enthalpy change
5. Use ∆H=Q/n
Chemical reactions that involve transfer of heat between system and surroundings
Exothermic
More heat energy is released than what is added
Bond making
Endothermic
Bond breaking
More heat energy is added than what is released