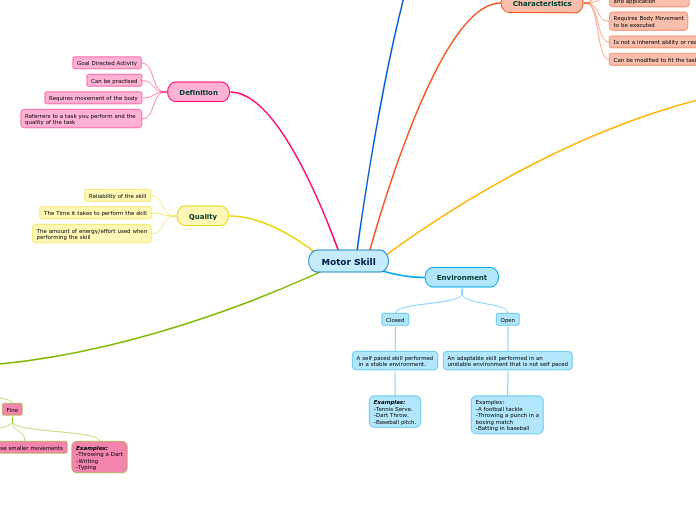
Motor Skill
Types
Specialised Motor Skills
Advanced/combinations of the fundamental
skills that can be applied to a specific sport/task
Fundamental Motor Skills
Foundational skills learned through
the lived experience
Characteristics
Performed for the sake of achieving
a specific goal
Voluntarily and deliberately
performed
Learned through practise
and application
Requires Body Movement
to be executed
Is not a inherent ability or reaction
Can be modified to fit the task required
Organisation
Discrete
A movement with a specified
beginning and ending. Short
in duration
Examples:
-Shooting a basketball
-Throwing a punch
-Kicking a soccer ball
Serial
Several individual discrete
actions linked together in
a specific order
Examples:
-A drive into a shot in
basketball
-A 1-2 punch combination
-Dribbling and kicking the
ball into a net
Continuous
A repeated movement with an
unclear beginning and ending.
Longer in duration
Examples:
-Running
-Swimming
Environment
Closed
A self paced skill performed
in a stable environment.
Examples:
-Tennis Serve.
-Dart Throw.
-Baseball pitch.
Open
An adaptable skill performed in an
unstable environment that is not self paced
Examples:
-A football tackle
-Throwing a punch in a
boxing match
-Batting in baseball
Definition
Goal Directed Activity
Can be practised
Requires movement of the body
Referrers to a task you perform and the
quality of the task
Quality
Reliability of the skill
The Time it takes to perform the skill
The amount of energy/effort used when
performing the skill
Classifications
Gross
Uses large muscle groups
Generates large power/force
Example:
-Jumping
-Sprinting
-Throwing a ball
Fine
Uses small muscle groups
Precise smaller movements
Examples:
-Throwing a Dart
-Writing
-Typing