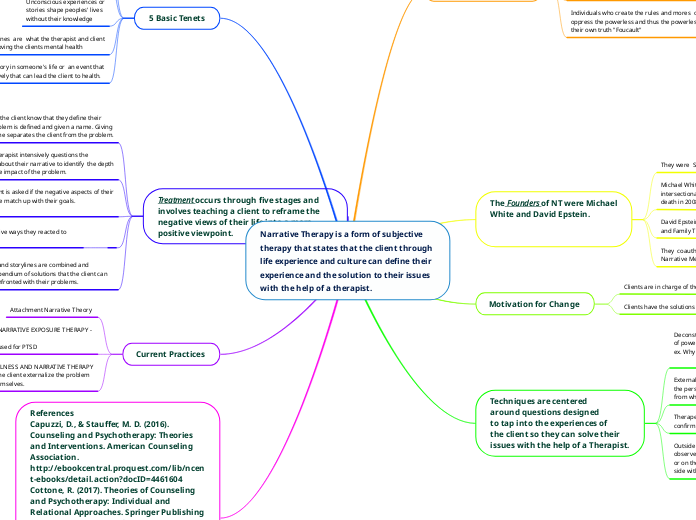
Narrative Therapy is a form of subjective therapy that states that the client through life experience and culture can define their experience and the solution to their issues with the help of a therapist.
5 Basic Tenets
Everyone Can Tell a Story
Only the Person telling the story
really knows what their story means
Unconscious experiences or
stories shape peoples' lives
without their knowledge
Negative Story Lines are what the therapist and client
work of for improving the clients mental health
There is always a good story in someone's life or an event that can be interpreted positively that can lead the client to health.
Treatment occurs through five stages and involves teaching a client to reframe the negative views of their life into a more positive viewpoint.
The Therapist lets the client know that they define their
problem. The problem is defined and given a name. Giving
the problem a name separates the client from the problem.
The therapist intensively questions the
client about their narrative to identify the depth
and the impact of the problem.
The client is asked if the negative aspects of their
narrative match up with their goals.
The client is asked to explore positive ways they reacted to their problems in the past.
All positive reactions and storylines are combined and integrated into a compendium of solutions that the client can use when they are confronted with their problems.
Foundations of Theory
Postmodern Theory that states that
reality is subjective.
The human defines the world, the world does not
define the human.
Deconstruction there is no fixed meaning to life the
user must define life on their own terms "Foucault"
Individuals who create the rules and mores of society use it to oppress the powerless and thus the powerless must define their own truth "Foucault"
The Founders of NT were Michael
White and David Epstein.
They were Social Workers
Michael White worked with
intersectional communities until his
death in 2008.
David Epstein worked in social work
and Family Therapy in New Zealand.
They coauthored a book on NT entitled
Narrative Means to Therapeutic Ends.
Motivation for Change
Clients are in charge of their own lives
Clients have the solutions within themselves
Techniques are centered
around questions designed
to tap into the experiences of
the client so they can solve their
issues with the help of a Therapist.
Deconstruction A therapist probes what systems
of power influenced the narrative the client has.
ex. Why do you believe that? or Who told you that?
Externalization - A therapist separates the problem from
the person so they do not think the problem is inseparable from who they are.
Therapeutic Documents - letters and documents that
confirm who the client is and affirm their story
Outside Witnessing - can be on the therapists side with
observers creating more probes for the therapists
or on the client's side with individuals on the client's
side with permission adding to the narrative of the client
Current Practices
Attachment Narrative Theory
NARRATIVE EXPOSURE THERAPY -
used for PTSD
MINDFULNESS AND NARRATIVE THERAPY
- helps the client externalize the problem
from themselves.