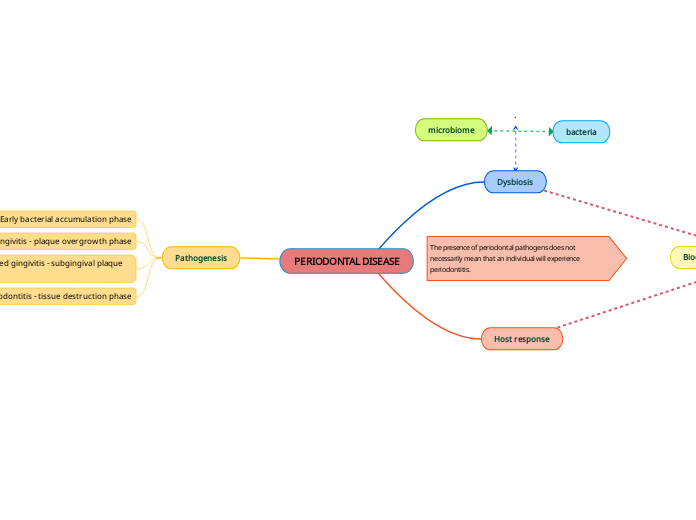
PERIODONTAL DISEASE
Dysbiosis
Host response
Pathogenesis
1. Early bacterial accumulation phase
2. Early gingivitis - plaque overgrowth phase
3. Established gingivitis - subgingival plaque phase
4. periodontitis - tissue destruction phase
The presence of periodontal pathogens does not necessarily mean that an individual will experience periodontitis.
bacteria
microbiome
Biochemical mediators of the immune system
Cytokines
- Recruit PMNs and macrophages to the infection site.
- Initiate tissue destruction and bone
Prostaglandins
- Increase vascular permeability allowing inmune cells and complement to move to the infection site
- PGE2 Alveolar bone destruction
MMPs
- Facilitate normal turnover of the connective tissue matrix
- Collagen destruction