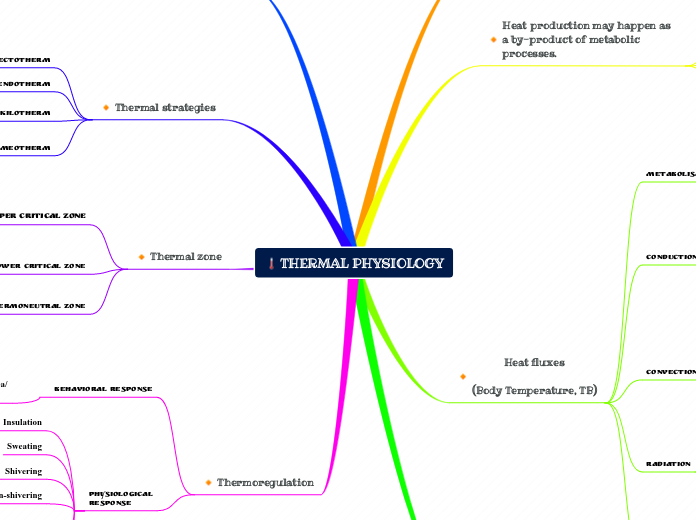
THERMAL PHYSIOLOGY
This includes adaptations in face of environmental challenges.
Heat fluxes
(Body Temperature, TB)
Metabolism
Main source of thermal energy
in the heat balance equation.
Conduction
Direct transfer of heat between two substances in contact with each other.
Heat flows from a region of ↑ temperature to
a region of lower temperature.
Rate depend on:
• area of physical contact
• different temperature
• thermal conductive properties
Convection
The heat is being carried from one point to another by a moving substance.
Exchanged depend on:
• thermal gradient
• rate of flow the fluid
• the conductivity of the fluid
Radiation
Transfer of thermal energy in the form of light waves, as exemplified by the heat we receive from the sun.
All bodies, including mammals, emit heat by radiation.
Evaporation
Water molecules absorb thermal energy from
an object when making the transition from
liquid to vapor.
Magnitude of heat loss depend on volume of
H2O and its heat of vaporization.
Thermal zone
Upper critical zone
Metabolic rate ↑ to induced a physiological
response to prevent overheating.
(Hyperthermia)
Lower critical zone
Metabolic rate ↑ to induced heat production.
(Hyphothermia)
Thermoneutral zone
Metabolic rate is minimal
(basal metabolic rate).
To investigate the biological
implications of temperature to the
function of living organisms.
Thermal strategies
Ectotherm
Rely mainly on external energy source.
Endotherm
Rely heavily on metabolic energy.
Poikilotherm
Body temperature varies directly with
environmental temperature.
Homeotherm
Maintain relatively constant
internal environmental.
Thermoregulation
Behavioral response
Surface area/
volume
Physiological
response
Insulation
Sweating
Shivering
Muscle contraction --> increase heat production.
Non-shivering
Metabolism --> increase heat production.
Circulating Adaptation
Vasolidation
Vasocontriction
Countercurrent Exchange
Heat production may happen as a by-product of metabolic processes.
The inefficient part of molecular transformations that causes part of the energy not to be used for work, but instead, lost as heat.
Thermal energy will not be transferred when there is thermal equilibrium.
Thermogenesis
An endothermic organism struggles in face of a colder-than-desirable ambient.