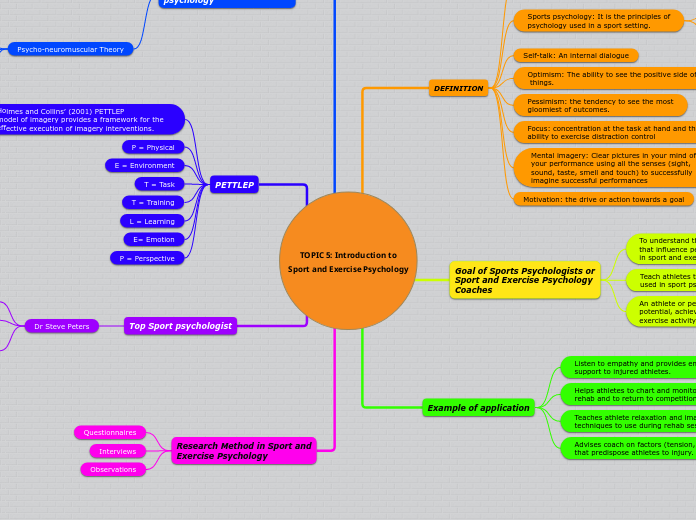
TOPIC 5: Introduction to
Sport and Exercise Psychology
DEFINITION
Psychology: The study of human and animal
behavior.
Sports psychology: It is the principles of
psychology used in a sport setting.
Athlete can gain the “mental edge” to reach their goals, recover from injury, or gain confidence.
Links the mental and physical aspects of training.
Self-talk: An internal dialogue
Optimism: The ability to see the positive side of
things.
Pessimism: the tendency to see the most
gloomiest of outcomes.
Focus: concentration at the task at hand and the
ability to exercise distraction control
Mental imagery: Clear pictures in your mind of
your performance using all the senses (sight,
sound, taste, smell and touch) to successfully imagine successful performances
Motivation: the drive or action towards a goal
Goal of Sports Psychologists or
Sport and Exercise Psychology
Coaches
To understand the social-psychological factors that influence people’s behavior and performance in sport and exercise activity.
Teach athletes techniques that are commonly used in sport psychology
An athlete or person has the ability to reach their potential, achieve peak performance in sport and exercise activity.
Example of application
Listen to empathy and provides emotional support to injured athletes.
Helps athletes to chart and monitor goals for rehab and to return to competition.
Teaches athlete relaxation and imagery techniques to use during rehab sessions.
Advises coach on factors (tension, life stress) that predispose athletes to injury.
Applications of clinical sport
psychology
Imagery
Involves the use of visualization procedures to
imagine physical performance, in absence of physical
movement.
It is also termed mental rehearsal or mental practice
Improve performance in activities that
require a lot of cognitive activity
Involves the production of
mental images in an opponent
Psycho-neuromuscular Theory
The use of imagery duplicates the motor pattern in the
brain, albeit on a smaller scale than with physical
practice.
This theory called the theory of muscle memory
Suggest that repeated mental practice allows the
performer to continue to activate the same brain systems
involved in movement.
PETTLEP
Holmes and Collins’ (2001) PETTLEP
model of imagery provides a framework for the effective execution of imagery interventions.
P = Physical
E = Environment
T = Task
T = Training
L = Learning
E= Emotion
P = Perspective
Top Sport psychologist
Dr Steve Peters
UK athletics team
British cycling team
Ronnie O’Sullivan-2012,2013 world snooker champion
Liverpool FC
England FA
Research Method in Sport and
Exercise Psychology
Questionnaires
Interviews
Observations