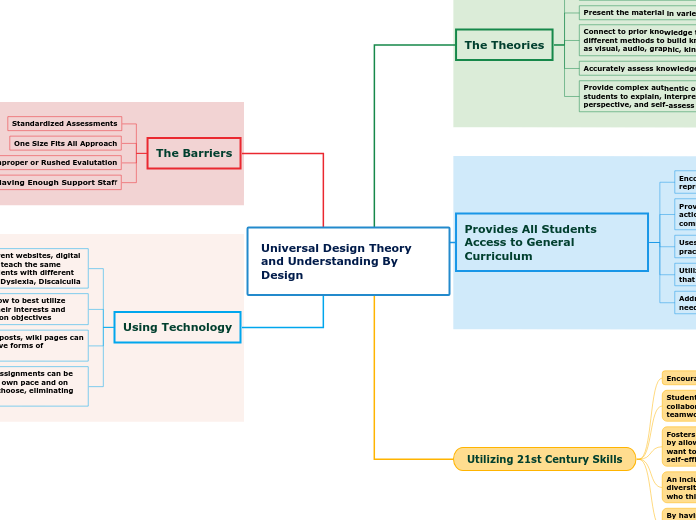
Universal Design Theory and Understanding By Design
The Theories
First Define Objectives/goals then plan assessments
Present the material in varied ways
Connect to prior knowledge then use different methods to build knowledge, such as visual, audio, graphic, kinetic, text
Accurately assess knowledge development
Provide complex authentic opportunities for students to explain, interpret, apply, shift perspective, and self-assess
Provides All Students Access to General Curriculum
Encourages multiple means of content representation
Provides different means of action/expression, uses multiple media for communication
Uses graduated levels of support for practice and performance. Scaffolding
Utilizes alternative forms of assessments that are more inclusive
Addresses the individual learner and their needs
Utilizing 21st Century Skills
Encourage individual choice and autonomy
Student centered learning encourages collaboration, communication and teamwork
Fosters creativity and problem solving skills by allowing students to choose how they want to be assessed, which helps develop self-efficacy
An inclusive classroom exposes students to diversity, different cultures and to people who think and act differently than them
By having students work in partners or groups with ELL's, and students with SLD's they are learning tolerance, acceptance and adaptability
The Barriers
Standardized Assessments
One Size Fits All Approach
Improper or Rushed Evalutation
Not Having Enough Support Staff
Using Technology
Teachers can use different websites, digital aids and technology to teach the same lesson to different students with different needs i.e. Autism, ELL, Dyslexia, Discalculia
Students can choose how to best utilize these tools based on their interests and needs to complete lesson objectives
Videos, podcasts, blog posts, wiki pages can all be used as alternative forms of assessments
Class lectures, notes, assignments can be viewed at the students own pace and on their own time if they choose, eliminating the "ticking clock"