View projection systems
Projections
Represents a three-dimensional object on a surface. Is the shadow of objects
Dihedral
The use of two projection planes reflects two views of a three-dimensional object.
three-dimensional object.
Pictorial projection
Projections that represent the object three-dimensionally, and show three
three of its faces.
Projection
Axonometric.
Represents objects by means of projection
projection on the three reference axes
Isometric projection.
Dimetric projection.
Trimetric projection.
Oblique
Two dimensions of the
object, are projected in true length
true length and the third dimension
third dimension with a
reduction coefficient, forming a 45° reduction angle.
Perspective
Represents objects as they are viewed by an observer.
Vanishing point, generates depth in the drawing.
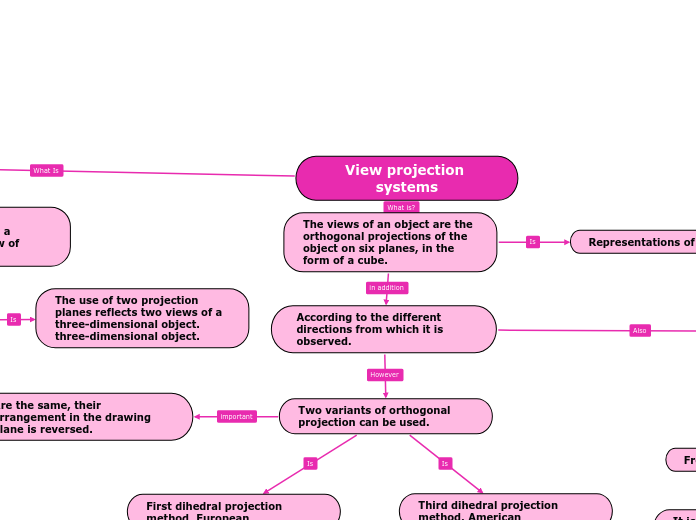
The views of an object are the orthogonal projections of the object on six planes, in the form of a cube.
Representations of the object
According to the different directions from which it is observed.
The six possible views of an object
View C
Right side view
View E
Bottom view
View F
Back view
View D
Left side view
View B
Top view or floor
View A
Front or elevation view
It is the view that provides
more information
Two variants of orthogonal projection can be used.
Are the same, their arrangement in the drawing plane is reversed.
First dihedral projection method, European
The plane of projection is located at the observer and the object.
First there is the observer, the object
object and finally the projection plane.
Place a floating stone inside a trihedron and project its views onto the faces.
Types of orthogonal projection
Axonometric projection
Isometric projection
Trimetric projection
Dimetric projection
Bounded projection
Projection in multiple views
Orthographic projection
Projection in the seventh octant
projection in the first octant
Third dihedral projection method, American
The object is located on the observer and the projection plane.
The image is projected at the observer's position inside the cube. it is represented at an angle of 90°.
First there is the observer, then the projection plane and finally the object.