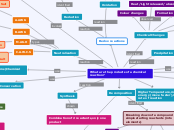
What are the products of a chemical reaction?
Decomposition
Breaking down of a compound into its simple starting reactants (into elements)
Light
AgBr => Ag + Br
(Light Energy)
Electrolysis
Bleach is made by the electrolysis of sale water
NaCl => Na + Cl
)Electrical Energy)
Thermal
CaCO3 => CaO + CO2
(Heat Energy)
Synthesis
Combination of 2 reactants, only one product
Chemical Changes
Colour changes
Heat/Light released/ absorbed
Formation of gas/ precipitate
Precipitate: does not dissolve, solid at room temperature
Production of odour
MISCONCEPTION:
Dissolution is a physical change (state change)
Students consider solid dissolved in liquid due to the solid 'disappearing'.
Higher Temperature, more kinetic energy (move faster), increase in the rate of reaction
Double Displacement
2 compounds to start; 2 compounds produced
Nature of the product, determined by solubility table
When a more reactive element takes the place of a less reactive one in a compound
AB + CD => AD + BC
The cations and anions switch elements
Separates Compounds
Obeys the Law of Mass Conservation
Balance Equations
Types and number of atoms are the same on each side of the equation
Rearrangement of atoms (Chemical Reaction)
Precipitation
When solutions mix together to form a solid
Lead Nitrate (l) + Potassium Iodide (l)
Lead Iodide(s) + Potassium Nitrate (l)
Neutralisation
C.A.W.C.S
Carbonate + Acid =>
Water + Carbon Dioxide + Salt
CuCO3 + 2HCl =>
CuCl2 + H2O + CO2
M.A.S.H
Metal + Acid => Salt + Hydrogen
Sn + 2HCl =>
SnCl2 + H2
B.A.W.S
Base + Acid => Water + Salt
Acid - Base titrations
AH + BOH => AB +H20
A.A.W.S
Acid + Alkail => Water + Salt
HCl + NaOH =>
H20 + NaCl
Processes taking occurring when Aboriginal & Torres Strait Islanders detoxify food
Cycad seeds
cycasin toxin
broken down and removed
rearranging atoms => new substance formation
number of atoms in reactants =
number of atom in products
subscripts
number of atoms in molecule => atomic properties
MISCONCEPTION:
that subscripts and coefficients are interchangeable
coefficients
number of molecules for reaction (completed)
Redox reactions
Oxidation
Fe + O => FeO
This is also known as Rusting
gain oxygen, remove hydrogen;
increase oxidation number, decrease electrons
Reduction
losing oxygen, gaining hydrogen;
decrease oxidation number, increase electrons