によって Brooklyn Babincsak 5年前.
318
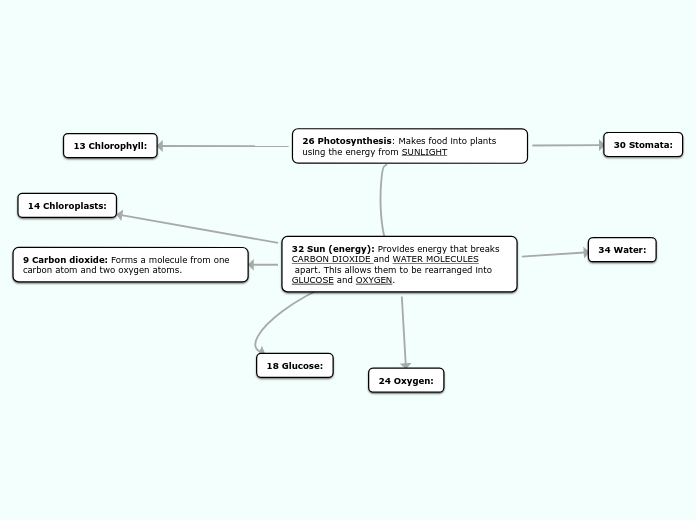
26 Photosynthesis: Makes food into plants using the energy from SUNLIGHT
によって Brooklyn Babincsak 5年前.
318

もっと見る
2 ATP synthase: Light reactions produce ATP which then enters the CALVIN CYCLE.
^