El niño y el Juego
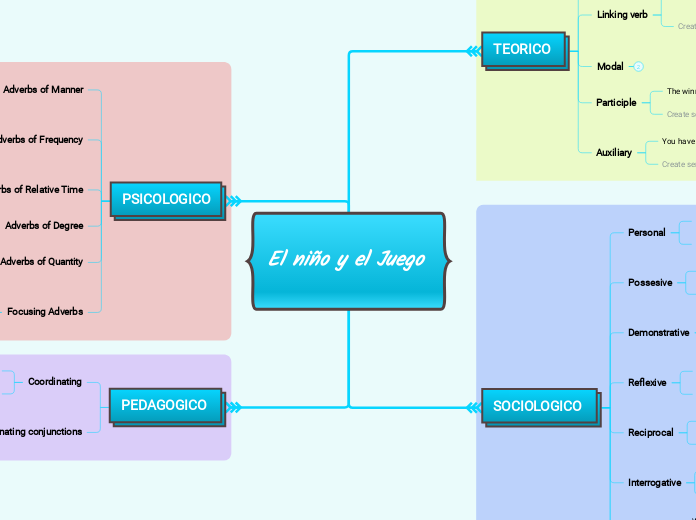
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
PEDAGOGICO
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
Subordinating conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Although it was raining, I went out.
Coordinating
Coordinating conjunctions always connect phrases, words, and clauses. They are: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
This stew is savory and delicious.
PSICOLOGICO
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
Focusing Adverbs
Especially, Specifically, Merely, Either
Adverbs of Quantity
A lot, Little, Much
Adverbs of Degree
The intensifiers strengthen adverbs adjectives and adverbs and down- toners make them weaker.
Adverbs of Relative Time
Just, Afterward, Soon, Currently
Adverbs of Frequency
Always, usually, Never
Adverbs of Manner
Carefully, Slowly
SOCIOLOGICO
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
Indefinite
Unlike demonstrative pronouns, which point out specific items, indefinite pronouns are used for non-specific things. This is the largest group of pronouns. All, some, any, several, anyone, nobody, each, both, few, either, none, one, and no one are the most common.
None, Several
Relative
Relative pronouns are used to add more information to a sentence. Which, that, who (including whom and whose), and where are all relative pronouns.
Which, Where
Interrogative
Interrogative pronouns are used in questions. Although they are classified as pronouns, it is not easy to see how they replace nouns. Who, which, what, where, and how are all interrogative pronouns.
Which, Who
Reciprocal
Reciprocal pronouns are used for actions or feelings that are reciprocated. The reciprocal pronouns are each other and one another.
Each other, one another
Reflexive
A reflexive pronoun ends with ...self or ...selves and refers to another noun or pronoun in the sentence (usually the subject of the sentence). The reflexive pronouns are myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
Itself, Himself
Demonstrative
Demonstrative pronouns are used to demonstrate (or indicate). This, that, these, and those are all demonstrative pronouns.
This, These
Possesive
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
His, Your
Personal
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
He, They
TEORICO
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
Auxiliary
An auxiliary verb helps the main (full) verb and is also called a 'helping verb.' With auxiliary verbs, you can write sentences in different tenses, moods, or voices.
You have been practicing hard.
Participle
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
The winning athlete gets a trophy.
Modal
A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. The main modal verbs in the English language are: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
I might go to the park if I get my homework done.
Linking verb
A linking verb connects the subject with a word that gives information about the subject, such as a condition or relationship.
You look exhausted after studying all night.
Full verb
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.
Create sentences
They have it.