によって JESUS DEL CARMEN MANJARREZ MORENO 5年前.
1245
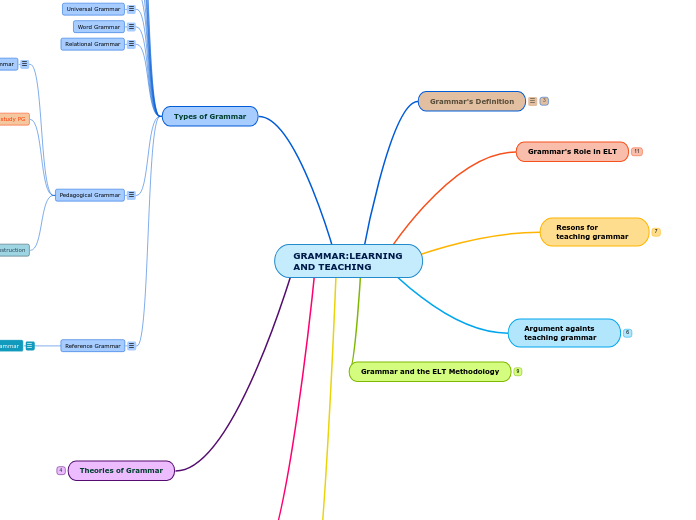
GRAMMAR:LEARNING AND TEACHING
によって JESUS DEL CARMEN MANJARREZ MORENO 5年前.
1245

もっと見る
Azar, B. (2007). Grammar-Based Teaching: A Practitioner's Perspective. TESL-EJ. 11(2). pp. 1-12.
Brown, D. (2007). Teaching by Principles: an Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy. Englewood Cliffs: Hall Regents.
Butler-Tanaka, P. (1998). What do you understand by the term consciousness-raising? To what extent is a grammar-translation approach based on consciousness-raising? University of Birmingham. Retrieved fromhttp://www.birmingham.ac.uk/Documents/college-artslaw/cels/essays/secondlanguage/PaulBT2.pdf on July 18th, 2013.
Hinkel, E. & Fotos, S. (Eds.). (2002). New Perspectives on Grammar Teaching in Second Language Classrooms.New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Publishers.
Hedge, T. (2000). Teaching and Learning in the Language Classroom. New York: Oxford University Press.
Mathews, P. H. (1997). The Concise Oxford Dictionary of Linguistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Prabhu, N. S. (1990). There Is No Best Method – Why?TESOL Quarterly, Vol. 24, No. 2.http://www.jstor.org/discover/10.2307/3586897?uid=3738664&uid=2129&uid=2&uid=70&uid=4&sid=21102543797057 Retrieved on July 18th, 2013.
Pullum, G. K. (n. d.). Learnability. Available at http://www.kornai.com/MatLing/learn.pdf Retrieved on July 18th, 2013.
Richards, J., Platt, J., and Platt, H. (1992). Dictionary of Language Teaching & Applied Linguistics. Harlow: Longman
Explanation of grammar rules: There are presctive and descriptive rules.
Prescriptive rules: Indicates how things need to be done.
Descriptive rules: Indicates how things are actually done.
Pedagogic rule: Rules written by linguists. In pedagogic rules we can find Rules of form and Rules of use.
Suggestions to give grammar explanations
Rules and explanation
Aspects to care about before explaining a rule:
Other written text
Dialogues: Use to present different grammatical structures.
Maps and drawings: Can be used to present some grammatical structures as prepositional phrases, questions, imperatives, and structures as 'there is' and 'there are'.
Objects: Using realia is motivating as it gives a kinaesthetic dimension to our teaching.
Charts: Useful for presenting patterns, clarifying grammatical associations and presenting the verb system.
ASPECTS TO CONSIDER IF AN ACTIVITY IS APPROPRIATE OR NOT.
ECONOMY: Has to do wiht using the time wisely. In grammar 'the shorter the better'.
EASE: The time that teachers invest in planning the lesson should be shorter that the class time. 'The easier the activity is to set up, the better it is.'
EFFICACY: Could be seen through the attention it arises and through the understanding the learners show by elicitation or answering questions, and finally it can be seen on how memorable the activity is for learners.
Conscious raising is an approach that helps learners to notice langugage features, then they can use those features to improve their acquisition of the language.
It is realted to learnability as if there is CR to identify mistakes (error corrections) then there would not be fossilization.
Attempts to apply the rigor of mathematics to peculiar regularities of human language, as:
It focuses on the process in the mind while communication is being used.
Scholars have long recognized that grammatical patterning reflects, however indirectly, a complex neurological system defined by the capacities and limitations of the human brain.
For linguist, a "Descriptive Grammar of a language' consyst of:
In contrast with prescirptivist, descriptive grammarians often focus on nonstandard dialects.
Prescription makes possible the standarization of languages, which makes communications easier. Codified language simplifies the learning and teaching of a language.
According to Loos et. al. (2004) 'a reference grammar is a prose-like description of the major grammatical constructions in a language, illustrated with examples.'
It is designed to teach someone about the language and to give readers a reference tool for looking up specific details of the language.
Odlin(1994:1) states that even though it could cover more areas 'pedagogical grammar usually denotes the types of grammatical analysis and instructions designed for the needs of second language students.'
The FOUR TYPES OF GRAMMAR has implications to teaching languages.
Discourse-Based Approaches
Interaction for Grammar Learning
In real communication one needs to understand and be understood; therefore, comprehensible output is essential for successful communication to take place.
Interaction is then needed for learners to increase their output and this contributes to learner internalization of L2 knowledge.
Noticing and Consciousness Raising
Focus on Form
It combines formal instructional and communicative language use.
It makes a distinction between:
Learner must notice, then process the target grammar structure in purely communicative input.
Communicative Language Teaching and Humanistic Approaches
Were developed in the lates 1970s and 1980s as communicative activities designed to give learners positive feelings toward the instructional process so that language acquisition was facilitated.
Cognitive Approaches
Functional Approach
It is a system of categories based on communicative needs of the learner and proposed a syllabus based on communicative functions.
It appeared to be opposite to structural syllabus but it still be structureal since certain structures are often associated with specfic functions.
Structural Grammar / Descriptive Linguistic
Was created as a reaction to Traditional Grammar Instruction. It offers another framework for the description of language through three systems, phonology, morphology and syntax.
Expert Guidance
Detailed evidence, in professional literature, suggests that teacher can make a difference.
Elli (1990b) concludes that 'Learners who receive formal instruction outperform those who do not; that is, they learn more rapidly and they reach higher levels of ultimate achievement.'
Traditional Grammar Instruction
Some of its characteristics are still in use as:
Fossilization
If students do not become capable analysts, their interlanguage competence will diverge from the target language grammar.
Learner Independece
Students have to become independent analyst of the target language if they are to deal with all the problems that their instructor lack time to cover in much detail.
Instructional Time
Time spent in a language course is only a fraction of what is needed to develop proficiency in a second language.
A therory of descriptive grammar in which syntactic operations (or relationships) rather that syntactic structures are used to define grammatical processes.
A theory of language structure which holds that grammatical knowledge is largely a body (or network) of knwoledge about words.
The system of categories, operations, and principles shared by all human languages and considered to be innate.
A therory of grammar that accounts for the constructions of a language by linguistic transformations and phrases structures.
The collection of prescritive rules and concepts about the structure of a language. We say that traditional grammar is prescriptive because it focuses on the distiction between what some people do with language and what they ought to do with it, according to a pre-stablished standard.
The study of the essential components of any human language
A description of the syntax of English as it is actually used by speakers in dialogues. It centers attention in language production.
The generative grammar stored in the brain that allows speaker to produce language that other speakers can understand. "All humans are born with the capacity for constructing a Mental Grammar." This is called Language Faculty.
Also known as tranformational-generative grammar or TG. It is a grammar (or set of rules) that indicates the structure and interpretation of sentences which native speakers of a language accept as belonging to the language.
Is the analysis and comparison of the grammatical structure of related languages. It stablishes the relationship among all languages.
Brown (2007:79) argues that in ordern to achieve communicative cometence language learners need to develop a combination of competencies:
Language use: Refers to the communicative meaning of a language
One use of third conditional is to express regrets.
Language Usage: Rules for making language.
The usage of third conditional is:
If + Past perfect + would + present perfect
Grammar is partly the study of what forms (or structures) are possible in a language. Traditionally, grammar has been concerned almost exclusively with analysis at the level of the sentences. Thus grammar is a description of the rules that govern how language's sentences are formed.