によって Jaime Gt 4年前.
407
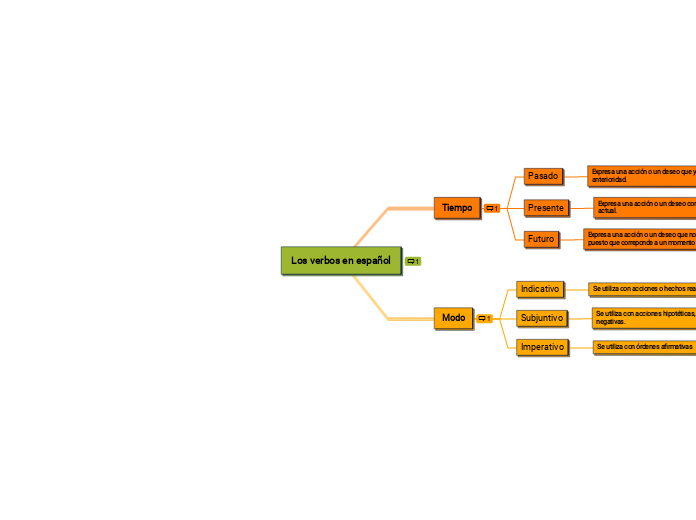
Los verbos en español
によって Jaime Gt 4年前.
407

もっと見る
As the main word in a sentence, the verb will generally describe an occurrence or an action.
El verbo es la parte de la oración o categoría léxica que expresa una acción, movimiento, existencia, consecución, condición o estado del sujeto.
Conditional verbs are used to create conditional sentences, which express hypothetical or unlikely situations. Conditional verbs can be used in the past, present, or future tense, and auxiliary verbs like can/could, will/would, and may/might are important in forming conditionals
El modo verbal corresponde a las
diferentes modalidades en que se expresan los tiempos verbales. Se
conocen el modo indicativo, que indica acciones concretas; el modo
subjuntivo, que indica posibilidades, y el imperativo, que representa
órdenes o instrucciones. Este último solo se manifiesta en un tiempo.
Ejemplos: LLega, quered, caed, come, salid, olvidad, cáete, comed.
An infinitive verb is essentially the base form of a verb with the word 'to' in front of it. When you use an infinitive verb, the 'to' is a part of the verb. It is not acting as a preposition in this case.
Ejemplos: Yo llegue, hubiera estado, queramos, cayera, comieras, salieran, olvidaran, te cayeras, hubieras comido.
Grammatical mood refers to the quality or form of a verb in a sentence. More specifically, mood denotes the tone of a verb in a sentence, so the intention of the writer or speaker is clear.
Ejemplos: Llegué, había estado, queríamos, cae, comes, salen, olvidarán, te caerás, habrás comido.
A participle is a form of a verb that can be used as an adjective or combined with the verb to be to construct different verb tenses.
Los tiempos verbales son modelos gramaticales de conjugación verbal
que sitúan en el tiempo una acción o un estado. En la lengua castellana,
los tiempos verbales se ven afectados por el aspecto y el modo.
El aspecto verbal o gramatical indica
si la acción es acabada o inacabada respecto al momento de la
enunciación. Se expresa con los términos perfecto (acción acabada),
imperfecto (acción inacabada) y pluscuamperfecto (una acción anterior a
otra).
An intransitive verb has two characteristics:
1.it is an action verb, expressing a doable activity
2.it will not have a direct object receiving the action
Ejemplos: Llegaré, viviré, te caerás, habrás cantado, estaría, caerá, habrás comido, querréis, saldrían, olvidarán.
In grammar, the voice of a verb describes the relationship between the action that the verb expresses and the participants identified by its arguments.
Ejemplos: Llego, vivo, te caes, cantas, estás, cae, comes, queremos, salen, olvidáis.
A transitive verb will only makes sense if it applies its action on an object.
Create sentences with examples!
Ejemplos: Llegué, viví, te caiste, cantaba, había estado, hubo caído, has comido, queríamos, salieron, olvidaron.