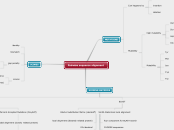
Pairwise sequence alignment
SCORES
scores
bit scores (normalized scores)
raw scores (calculate from substitution matrix)
gap penalty
extension - elongate gap
opening - inroduce gap
mismatch
identity
SCORING MATRICES
BLAT
more than 95% similarity
design to rapidly align longer nucleotide sequence
500 times faster than BLAST
BLAST-like alignment tool
BLAST
Smith-Waterman local alignment
CHOOSE optional parameters
output format
word size
expect value
E = Kmn e-λS
Extreme Value Distribution (EVD)
substitution matrix
Turn filtering on/off
Organism
different for every blast program
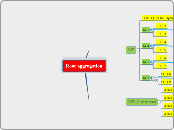
CHOOSE database
pnv_nr
Subtopic
Pat
Pdb
RefSeq
Swisprot
Month
nr
SELECT BLAST program
tblastx
tblastn
blastx
blastn
blastp
CHOOSE sequences
four component for BLAST search
Blocks Substitution Matrix (Henikoff)
X% identical
local alignment (distantly related protein)
PAM
Percent Accepted Mutations (Dayhoff)
global alignment (closely related protein)
X% divergence
PAM1
one PAM (unit of evolution) =
1% amino acids changed between two proteins
at least 85% identical
probability of occurance
+
percent accepted mutations
=
mutation probability matrix
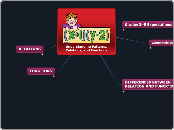
MUTATIONS
Mutability
Trp
Cys
Leu
Phe
Tyr
high mutability
Glu
Asp
Ser
Asn,
Can happens by
deletion
insertion
substitution