によって Bri Marquez 5年前.
187
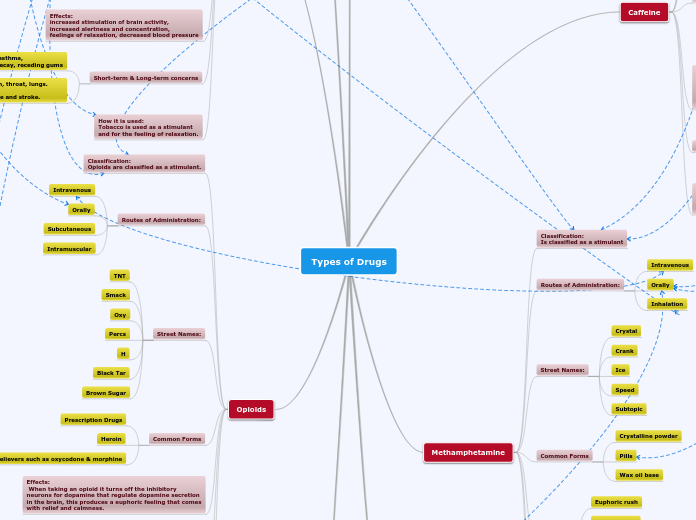
Types of Drugs
Inhalants and psychedelics represent two distinct categories of drugs with varying effects and concerns. Inhalants, classified as depressants, induce a rapid sense of euphoria and a head high when inhaled, commonly using everyday items like gasoline or hair spray.