によって Manisha Sidhu 4年前.
288
War & Conflict
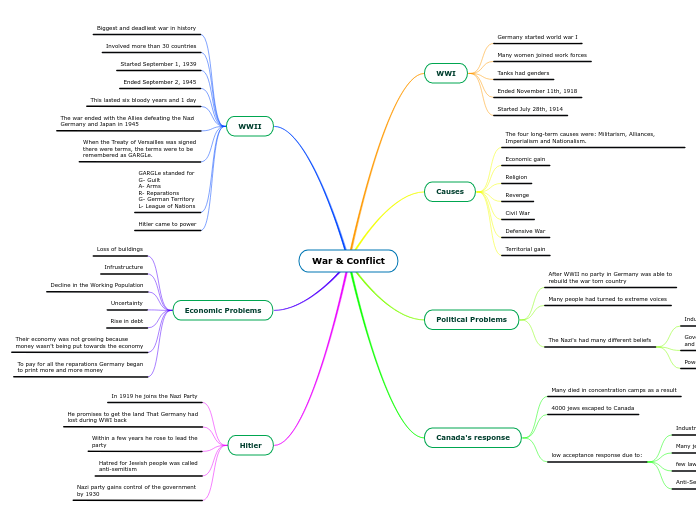
War & Conflict
Hitler
Nazi party gains control of the government
by 1930
Hatred for Jewish people was called
anti-semitism
Within a few years he rose to lead the
party
He promises to get the land That Germany had
lost during WWI back
In 1919 he joins the Nazi Party
Economic Problems
To pay for all the reparations Germany began
to print more and more money
Their economy was not growing because
money wasn't being put towards the economy
Rise in debt
Uncertainty
Decline in the Working Population
Infrustructure
Loss of buildings
WWII
Hitler came to power
GARGLe standed for
G- Guilt
A- Arms
R- Reparations
G- German Territory
L- League of Nations
When the Treaty of Versailles was signed
there were terms, the terms were to be
remembered as GARGLe.
The war ended with the Allies defeating the Nazi
Germany and Japan in 1945
This lasted six bloody years and 1 day
Ended September 2, 1945
Started September 1, 1939
Involved more than 30 countries
Biggest and deadliest war in history
Canada's response
low acceptance response due to:
Anti-Semitism movement in Canada
few lawyers, professors and teachers
Many jews had to hide their identities
Industries refused to hide jews
4000 jews escaped to Canada
Many died in concentration camps as a result
Political Problems
The Nazi's had many different beliefs
Power of the military should be increased
Government should be run by army
and wealthy
Industry should be privately owned
Many people had turned to extreme voices
After WWII no party in Germany was able to
rebuild the war torn country
Causes
Territorial gain
Defensive War
Civil War
Revenge
Religion
Economic gain
The four long-term causes were: Militarism, Alliances, Imperialism and Nationalism.
WWI
Started July 28th, 1914
Ended November 11th, 1918
Tanks had genders
Many women joined work forces
Germany started world war I

