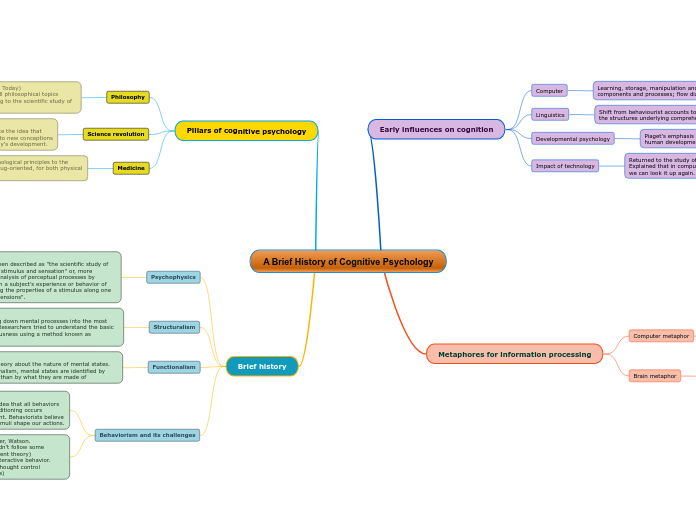
A Brief History of Cognitive Psychology
Pillars of cognitive psychology
Philosophy
(385 BC- Today)
Covers all philosophical topics pertaining to the scientific study of cognition
Science revolution
(1500 - 1700)
The scientific revolution did more than create the idea that psychology might be a science, it gave rise to new conceptions of mind and body fundamental to psychology's development.
Medicine
Refers to the application of psychological principles to the practice of medicine, primarily drug-oriented, for both physical and mental disorders.
Brief history
Psychophysics
(1860)
Psychophysics has been described as "the scientific study of the relation between stimulus and sensation" or, more completely, as "the analysis of perceptual processes by studying the effect on a subject's experience or behavior of systematically varying the properties of a stimulus along one or more physical dimensions".
Structuralism
(20th century)
Focused on breaking down mental processes into the most basic components. Researchers tried to understand the basic elements of consciousness using a method known as introspection.
Functionalism
(19th century)
Functionalism is a theory about the nature of mental states. According to functionalism, mental states are identified by what they do rather than by what they are made of
Behaviorism and its challenges
(1913)
It is a theory of learning based on the idea that all behaviors are acquired through conditioning. Conditioning occurs through interaction with the environment. Behaviorists believe that our responses to environmental stimuli shape our actions.
Most important theorists: Pavlov, Skinner, Watson.
-Organisms tend to misbehave, they didn't follow some predictions on behavior (infant attachment theory)
-Failed to accurately predict complex interactive behavior.
- Could not account for the behavior / thought control relationship. ( theory of ironic processes)
Early influences on cognition
Computer
Learning, storage, manipulation and memory. Internal components and processes; flow diagrams
Linguistics
Shift from behaviourist accounts to theories that emphasized the structures underlying comprehension (Chomsky)
Developmental psychology
Piaget's emphasis on the internal structures and processes of human development
Impact of technology
Returned to the study of mental processes.
Explained that in computers key board inputs information and we can look it up again.
Metaphores for information processing
Computer metaphor
The computer gave cognitive psychologists a metaphor, or analogy, to which they could compare human mental processing. The use of the computer as a tool for thinking how the human mind handles information is known as the computer analogy.
Brain metaphor
The brain metaphor describes organizations as comprised of thinking, learning, and active participants that gather information and apply it in various ways. Like rational creatures, organizations also 'think', adapt, and evolve.