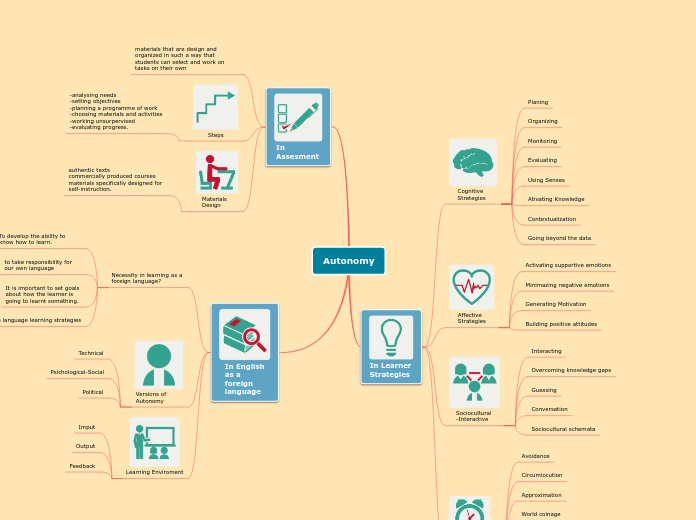
Autonomy

In Learner Strategies

Cognitive Stretegies
Planing
Organizing
Monitoring
Evaluating
Using Senses
Ativating Knowledge
Contextualization
Going beyond the data

Affective Strategies
Activating supportive emotions
Minimazing negative emotions
Generating Motivation
Building positive attitudes

Sociocultural-Interactive
Interacting
Overcoming knowledge gaps
Guessing
Conversation
Sociocultural schemata

Compensatory Strategies
Avoidance
Circumlocution
Approximation
World coinage
Nonverbal signals
Prefabricated paterns
Code switching
keeping the floor

In Assesment
materials that are design and organized in such a way that students can select and work on tasks on their own

Steps
-analysing needs
-setting objectives
-planning a programme of work
-choosing materials and activities
-working unsurpervised
-evaluating progress.

Materials Design
authentic texts
commercially produced courses
materials specifically designed for self-instruction.

In English as a foreign language
Necessity in learning as a foreign language?
To develop the ability to know how to learn.
to take responsibility for our own language
It is important to set goals about how the learner is going to learnt something.
Choose language learning strategies

Versions of Autonomy
Technical
Psichological-Social
Political

Learning Enviroment
Imput
Output
Feedback