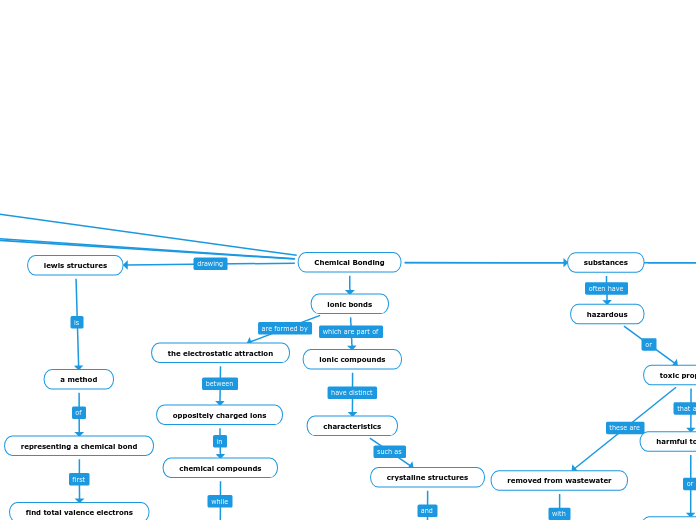
Chemical Bonding
substances
hazardous
toxic properties
harmful to health
the environment
plants and animals
display symptoms
humans
toxic levels of chemicald
their effect
health
age, weight, and preexisting conditions
removed from wastewater
chemical precipitation
ion exchange
heavy metals (cadmium, arsenic, mercury)
properly disposed of
lab disposal container
down the sink
heavy metals
water systems
wildlife
heavy metal poisoning
interfering with ecosystems
humans
reproductive damage
metal toxicity
infertility and death
chemical solutions
sulfuric acid
iron(ll) sulfate
a medication
the logic
not flushing medication
not dumping chemicals
the sink
lewis structures
a method
representing a chemical bond
find total valence electrons
the skeleton structure
single bonds
remaining valence electrons
multiple bonds
electron octets
full
brackets and charge
electrons
outermost electron shell
ionic bonds
the electrostatic attraction
oppositely charged ions
chemical compounds
covalent bonds
atoms
an electron pair
covalent compounds
characteristics
low melting/boiling point
strong insulators
insolubility
ionic compounds
characteristics
crystaline structures
high melting/boiling point
water solubility
conductivity
brittleness
predicting the type
bond
be done
looking at
the electronegativity
elements.
elements
large difference
electronegative charges
an ionic bond
smaller difference
covalent bonds
activity series
list of elements
reactivity level
decreasing ease
oxidation
increasing ability
take an electron
chemical compunds
the IUPAC nomenclature system
find the longest carbon chain
attached groups
number the chain
a name/number to each group
chemical compound formulae
the positive ion/atom
the negative second
NaCl