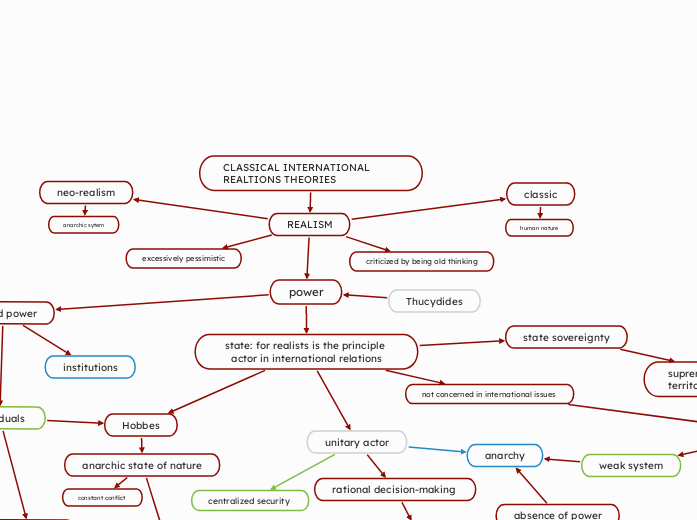
CLASSICAL INTERNATIONAL REALTIONS THEORIES
REALISM
power
state: for realists is the principle actor in international relations
not concerned in international issues
international system
distrubution of power
unipolar system
single power
bipolar system
two powers
multipolar system
3+ powers
Hobbes
anarchic state of nature
lack of limits
individualist behavior on the nature of the human being
To escape this perilous condition
everyone has the right to everything
constant conflict
state sovereignty
supreme authority over their territory
excessively pessimistic
criticized by being old thinking
classic
human nature
neo-realism
anarchic sytem
institutions
individuals
the leaders
political behavior
power and deception
political realism
Machiavellianism
denies the relevance of ethics in politics
justified immoral actions in politics
moral traditions
human nature
unitary actor
rational decision-making
national interest
survival
flexible alliances
balance of power
prudent strategy
anarchy
centralized security
amoral
limited power
appetite for power
selfishness
weak system
Thucydides
relation
state
provides protection
maintains order
preventing the return to the state of nature
individuals
social contract
surrender some freedoms
submit to the authority