Tremor
Postural instability
Akinesia
severe bradykinesia
Cognitive Disorders (Impairment, Dementia)
Gradually discontinue anticholinergic medications
Treat with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as donepezil, rivastigmine or galantamine
Mood Disorders (Anxiety, Depression)
Depression
Treat with SSRIs/TCAs
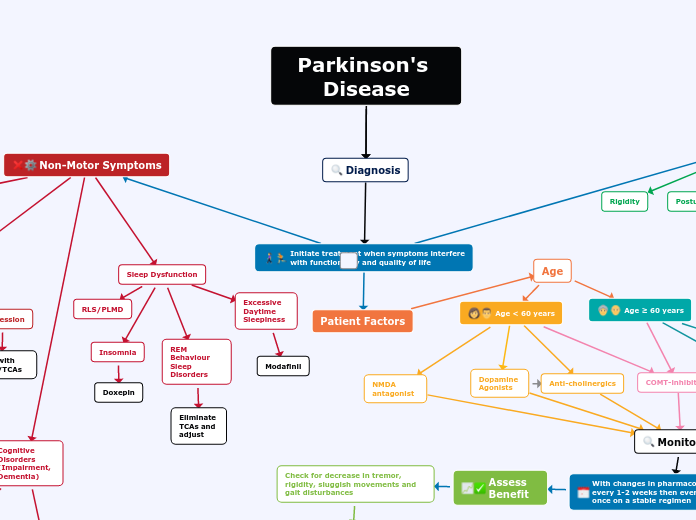
Sleep Dysfunction
Insomnia
Doxepin
REM Behaviour Sleep Disorders
Eliminate TCAs and adjust
RLS/PLMD
Motor Symptoms
Dopamine Agonists
Anti-cholinergics
MAO-B inhibitors
Rigidity
Initiate treatment when symptoms interfere with functionality and quality of life
Patient Factors
Age
Age < 60 years
NMDA antagonist
COMT-inhibitors
Age ≥ 60 years
Dopamine precursor + decarboxylase
Non-Motor Symptoms
mild bradykinesia
Monitoring
With changes in pharmacotherapy follow-up every 1-2 weeks then every 3-6 months once on a stable regimen
Assess Benefit
Check for decrease in tremor, rigidity, sluggish movements and gait disturbances
Suboptimal Response
Consider, increasing the dose of the agent; initiating Levodopa/Dopamine agonist; adding therapy (i.e. dopamine agonist, MAO-B i, COMT-i, etc); changing time of administration/formulation
Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
Modafinil
Autonomic Dysfunction (GI disorders, Orthostatic Hypotension, Sexual Dysfunction, Urinary Incontinence)
GI Disorders
PEG, stool softeners, Lactulose, Domperidone
Orthostatic Hypotension
Fludrocortisone, Domperidone, midodrine
Sexual Dysfunction
Sildenafil
Urinary Incontinence
Oxybutynin, Tolterodine, Propantheline
Anxiety
Adjust dopaminergic drugs
Treat with SSRIs/TCAs/Benzodiazepines
Lower dose of Levodopa
Assess for Complications
Motor Complications "Wearing Off"
-increase Levodopa dose if patient does not have dyskinesia or increase frequency if patient has dyskinesia. Addition of a dopamine agonist, COMT or MAO-B inhibitor can also be considered.
Dyskinesias
- Increase (diphasic) or reduction (peak-dose) in levodopa dose
- Add DA
- Increase dose of DA if on concurrent therapy
- Add Amantadine
Freezing
- Increase levodopa dose
- Add DA or MAO-B
- Non Pharm → sensory cues + devices
Hallucinations
- Gradually decrease dose + eliminate PD medications w/ potential for hallucinations in the following order : Anticholinergics, MAO-B inhibitors, DA, Levodopa
- If above fails, consider antipsychotics (quetiapine, clozapine)