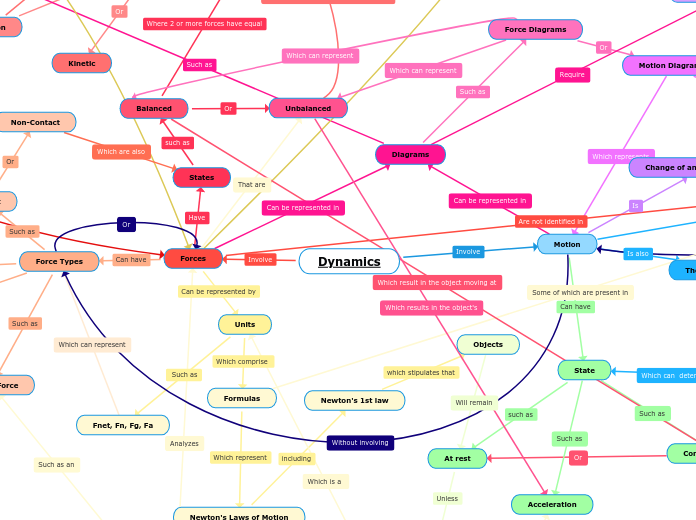
Dynamics
Motion
The change of an object's location
Time
Change of an object's position
A set origin
A positive and negative
State
At rest
Acted upon
External Force
Forces
States
Balanced
Unbalanced
Magnitude
Direction
Equal
Force Pair
Force Types
Contact
Non-Contact
Normal force
Friction
Static
Kinetic
Coefficient
Applied Force
Gravitational Force
Units
Formulas
Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's 1st law
Objects
Newton's 2nd Law
Net Force
Fnet = m • a
a = Fnet / m
Newton's 3rd Law
Fnet, Fn, Fg, Fa
Kinematics
Diagrams
Force Diagrams
Motion Diagrams
Interaction Diagrams
Interaction
System
Set list