ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
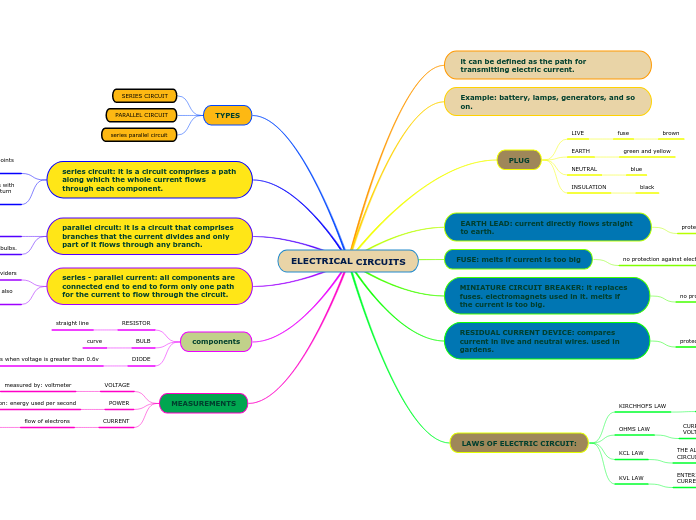
it can be defined as the path for transmitting electric current.
Example: battery, lamps, generators, and so on.
PLUG
LIVE
fuse
brown
EARTH
green and yellow
NEUTRAL
blue
INSULATION
black
EARTH LEAD: current directly flows straight to earth.
protects against electric shocks
FUSE: melts if current is too big
no protection against electric shock
MINIATURE CIRCUIT BREAKER: it replaces fuses. electromagnets used in it. melts if the current is too big.
no protection against electric shock.
RESIDUAL CURRENT DEVICE: compares current in live and neutral wires. used in gardens.
protects against electric shocks
LAWS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUIT:
KIRCHHOFS LAW
OHMS LAW
CURRENT THROUGH A CIRCUIT IS PROPORTIONAL TO THE VOLTAGE ACROSS THE CONDUCTOR
KCL LAW
THE ALGEBRAIC SUM OF VOLTAGE AT NODE IN A CLOSED CIRCUIT IS ZERO.
KVL LAW
ENTERING CURRENT AT NODE IS EQUAL TO LEAVING CURRENT AT NODE.
TYPES
SERIES CIRCUIT
PARALLEL CIRCUIT
series parallel circuit
series circuit: it is a circuit comprises a path along which the whole current flows through each component.
used for: it provides exactly one path between any two points for electric current.
examples: often lawnmowers have two switches in series with each other so both need to switch before the mower will turn on.
parallel circuit: it is a circuit that comprises branches that the current divides and only part of it flows through any branch.
used for: to keep electricity flowing when one pathway is interrupted.
example: light fixtures that use multiple bulbs.
series - parallel current: all components are connected end to end to form only one path for the current to flow through the circuit.
used for: voltage dividers
For example: multiple bulbs are connected with wire and also some are in the loop
components
RESISTOR
straight line
BULB
curve
DIODE
current only flows when voltage is greater than 0.6v
MEASUREMENTS
VOLTAGE
measured by: voltmeter
connected in parallel
units: volts(V)
POWER
definition: energy used per second
units: watts(W)
CURRENT
flow of electrons
measured by: ammeter
units: ampere(A)