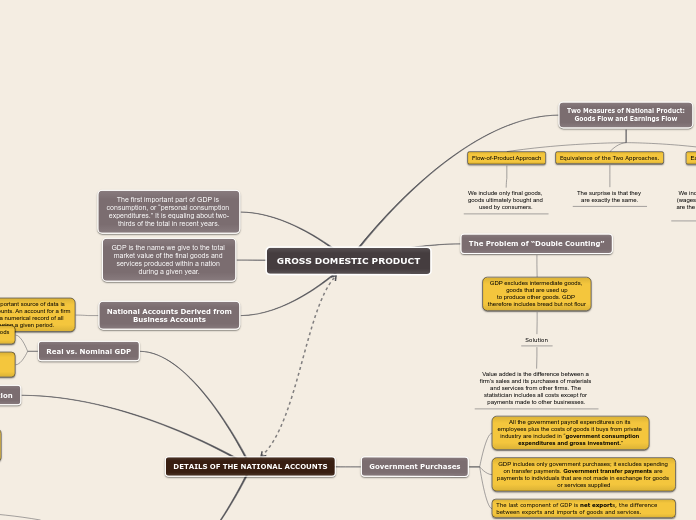
GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT
Two Measures of National Product:
Goods Flow and Earnings Flow
Flow-of-Product Approach
We include only final goods, goods ultimately bought and used by consumers.
Equivalence of the Two Approaches.
The surprise is that they are exactly the same.
Earnings or Income Approach
We include the total of factor earnings (wages, interest, rents, and profits) that are the costs of producing society’s final
products.
The Problem of “Double Counting”
GDP excludes intermediate goods, goods that are used up
to produce other goods. GDP therefore includes bread but not flour
Solution
Value added is the difference between a firm’s sales and its purchases of materials and services from other firms. The statistician includes all costs except for payments made to other businesses.
The first important part of GDP is consumption, or “personal consumption expenditures.” It is equaling about two-thirds of the total in recent years.
GDP is the name we give to the total market value of the final goods and services produced within a nation during a given year.
National Accounts Derived from
Business Accounts
The most important source of data is business accounts. An account for a firm or nation is a numerical record of all flows during a given period.
DETAILS OF THE NATIONAL ACCOUNTS
Real vs. Nominal GDP
Nominal GDP represents the total money value of final goods and services produced in a given year
Real GDP removes price changes from nominal GDP and calculates GDP in terms of the quantities of goods and services.
Investment and Capital Formation
investment consists of the additions to the nation’s capital stock of buildings, equipment, software, and inventories during a year.
Net vs. Gross Investment.
Thus to estimates the increase in the capital stock we measure net investment. Net investment is always births of capital (gross investment) less deaths of capital (capital depreciation)
This gross investment includes all the machines, factories, and houses built during a year
Gross Domestic Product, Net Domestic
Product, and Gross National Product
GDP includes gross investment, which is net investment plus depreciation. By subtracting depreciation from GDP we obtain net domestic product (NDP).
NDP = GDP - depreciation
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN GNP AND GDP?
GNP is the total output produced with labor or capital owned by U.S. residents, while GDP is the output produced with labor and capital located inside the United States.
Government Purchases
All the government payroll expenditures on its employees plus the costs of goods it buys from private industry are included in “government consumption expenditures and gross investment.”
GDP includes only government purchases; it excludes spending on transfer payments. Government transfer payments are payments to individuals that are not made in exchange for goods or services supplied
The last component of GDP is net exports, the difference between exports and imports of goods and services.