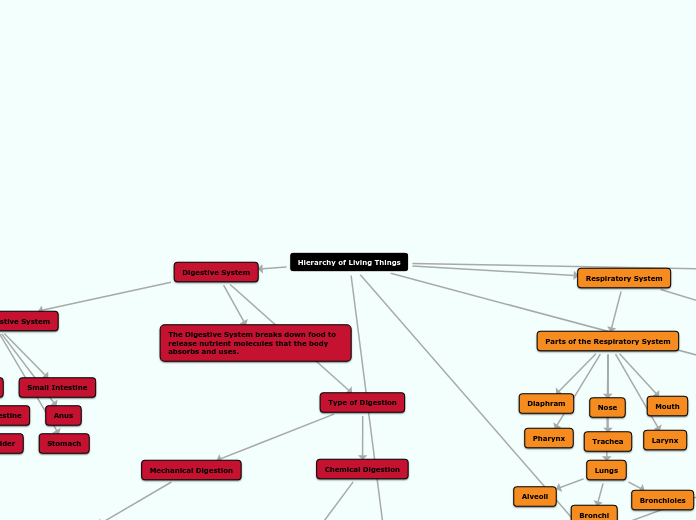
Hierarchy of Living Things
Digestive System
Parts of the Digestive System
Mouth
Esophagus
Small Intestine
Liver
Large Intestine
Anus
Pancreas
Gallbladder
Stomach
Digestive System Image
The Digestive System breaks down food to release nutrient molecules that the body absorbs and uses.
Type of Digestion
Chemical Digestion
Food is broken down with chemicals. enzymes break the chemical bonds that hold food particles together. This allows food to be broken down into small, digestible parts
Mechanical Digestion
Food is broken down by chewing, tearing, grinding of teeth and the stomach. It is a purely physical process controlled by you and it makes food smaller to have more area.
Respiratory System
Parts of the Respiratory System
Diaphram
Nose
Mouth
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Lungs
Alveoli
Bronchi
Bronchioles
The Respiratory System is responsible with all the organs to help us breathe oxygen in and removing carbon dioxide.
Gas Exchange
Alveoli are surrounded with capitulary networks that contain blood.
Oxygen makes it's way in by getting inhaled and carbon dioxide gets diffused out with exhalation. Breathing in allows the lungs to expand and breathing out closes them down slowly and exchange occurs.
Respiratory System Image
The Circulatory System allows oxygen to be delivered into cells and takes out the carbon dioxide buildup.
Inhalation
1. Diaphragm moves down as it contracts 2. Rib cage has in and out movements 3. Chest capacity increases 4. Air rushes in
Exhalation
1. Diaphragm moves up 2. Rib cage goes in and down 3. Chest capacity decreases 4. Air rushes out
Circulatory System
Parts of the Circulatory System
Blood
The Heart
Left and Right side
Blood Vessels
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Circulatory System is made up from blood vessels that carry blood away and towards the heart. The circulatory system carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells, and removes carbon dioxide.
Circulatory System Image
Organs
Stomach
Liver
Heart
Lungs
Tissue
Animal cells have different types of tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Columnar Epithelia
Columns of cells that line the organs.
Tissue Image
Nervous Tissue
Neurons send signals and receive them
Skeletal Muscle
Movement is allowed and Cells line up in the same direction.
Smooth Muscle
Blood vessels and walls of organs contracts slowly
Cardiac Muscle
Contract as a unit
Connective Tissue
Support and protects the cells and tissues
Bone
Movement and Support
Blood
Red and White blood cells , Transports nutrients and oxygen , Takes care of bacteria and viruses
Fat
Stores energy and is like a coat for organs
A group of cells that have fanmilar functions with the same goal of helping the body
Cell
Cell Cycle
A cell cycle is a series of events that takes place in a cell as it grows and divides. ... The cell then leaves interphase, undergoes mitosis, and completes its division.
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells
Cell Divison
Animal Cells
Animal cells are enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
Animal Cell Parts
Nucleus
Ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes
Mitochondria
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Plant Cells
Plant cells are the basic unit of life in organisms and Plant cells have special organelles called chloroplasts, which create sugars with photosynthesis.
Animal Cell Image
Plant Cell Image