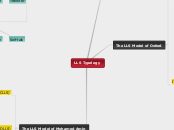
LLS Typology
The LLS Model of Oxford
Direct strategies
Memory strategies
Creating mental linkages
Reviewing well
Employing action
Cognitive strategies
Practice
Receiving and sending messages
Analyzing and reasoning
Compensation strategies
Creating structure for input and output
Indirect strategies
Metacognitive strategies
Arranging and planning your learning
Centering your learning
Evaluating your learning
Affective strategies
Lowering your anxiety
Encouraging yourself
Taking your emotional temperature
Social strategies
Asking questions
Cooperating with others
Empathizing with others
The LLS Model of O'Malley and Chamot
Metacognitive strategies
Advance organization
Advance preparation
Organizational planning
Selective attention
Self-monitoring
Self-evaluation
Self-management
Cognitive strategies
Resourcing
Grouping
Note taking
Summarizing
Deduction
Imagery
Auditory representation
Elaboration
Transfer
Inferencing
Socio-affective strategies
Questioning for clarification
Cooperation
Self-talk
The LLS Model of Mohamed Amin
Classroom LLS (CLLS)
Sitting near students who are proficient in the target language
Asking for a friend's or teacher's clarification
answer silently to oneself
Out-Of-Class LLS (OLLS)
Conversing in English with the parents at home
Discussing with friends after class
Watching English movies
Exam LLS (ELLS)
Learner's preparation leading to an examination such as joining a discussion group
Doing exercises in workbooks
Memorizing essay format