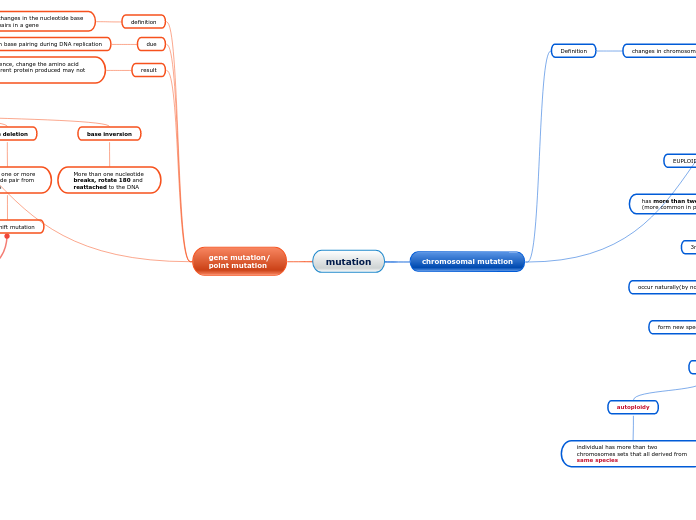
mutation
gene mutation/
point mutation
definition
changes in the nucleotide base
pairs in a gene
due
mistake in base pairing during DNA replication
result
changes of codon in mRNA. Hence, change the amino acid sequence and the protein.Different protein produced may not function as normal
type
base substitution
one nucleotide pair is replaced with
another nucleotide pair in the
DNA sequence
lead- silent, missense, nonsense mutation
SILENT MUTATION
base substitution nucleotide pair of DNA
has no effect on the encoded protein
change in nucleotide but translated
same amino acid
changes codon on mRNA
codes for the same amino acid
MISSENSE MUTATION
cause frameshift mutation
amino acid changes to another
amino acid
results in ONE WRONG CODON
and ONE WRONG AMINO ACID
in polypeptide
less active protein
eg: SICKLE CELL
ANEMIA(RBC shape
like a crescent)
DNA- CTT replaced CAT
mRna-codon GAA replaced GUA
polypeptide- glutamic acid replaced valine
symptoms sickle
cell anemia
*Hb-stiff, tend to accumulate at
blood capillary
*fatal form of anemia
*organ damages
*physical weakness
NONSENSE MUTATION
changes mRNA into
a stop codon
translation terminated
produce shorter
polypeptide
lead to non-functional proteins
base insertion
Addition of one or a more nucleotide pair
into the DNA
frameshift mutation
base deletion
Loss of one or more
nucleotide pair from
the DNA
frameshift mutation
base inversion
More than one nucleotide
breaks, rotate 180 and
reattached to the DNA
chromosomal mutation
Definition
changes in chromosomal structure or chromosomal number
type
CHRMOSOMAL NUMBER
ALTERATIONS
change in number
EUPLOIDY/POLYPOIDY
has more than two sets of chromosomes
(more common in plant)
3n,4n,5n,
occur naturally(by non-disjunction or induction)
form new species better qualities
type
autoploidy
individual has more than two
chromosomes sets that all derived from
same species
alloploidy
individual has more than two
chromosomes sets that derived from
different species
ANEUPLOIDY
chromosomal EXTRA or MISSING from
normal set
cause-non-disjunction during meiosis
(anaphaseI,II)
non-disjunction-failure of a homologous chromosomes
or sister chromatid to separate and move to opposite poles
occur in autosome and sex-chromosomes
eg: 2n-1monosomy,2n+1trisomy
CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION
change in structure