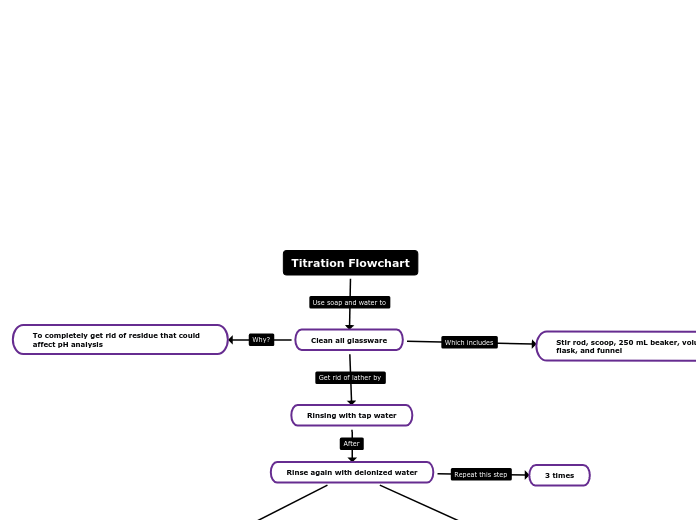
Titration Flowchart
Clean all glassware
Stir rod, scoop, 250 mL beaker, volumetric flask, and funnel
Rinsing with tap water
Rinse again with deionized water
3 times
Primary Standard
Measure and record mass of Borax
Need to have a reference molar mass for titration
250 mL beaker
Mix solute until all Borax solute is dissolved
Solution into volumetric flask by decanting
Funnel on top of beaker
Place glass rod on top of beaker
Pour solution into flask carefully
Borax solution in volumetric flask reaches meniscus of fill line
Diluted HCL solution reaches
meniscus of fill line
Begin standardization
Needed molar concentration of titrant is determined
Standardized HCL into burette
Begin Titration
Erlenmeyer Flask
Until solution changes colour completely
Solution has reached end point due to a pH change, moles of titrant exceed moles of analyte
Equivalence Point
Moles of titrant equal moles of analyte, right before endpoint
1:1 molar ratio, ICE box, Kb/Ka
Concentration of ammonia
C1V1=C2V2
It helps determine a more accurate concentration of the titrant for calculations
n=m/mm, c=n/v
All solution is transferred
Beaker with deionized water
3x with deionized water
Deionized water
It reaches fill line
Titrant
Volume of concentrated HCL solution needed to make up given volume of the dilute HCL solution stoichiometrically
C1V1=C2V2
Need to know the molar concentration of diluted solution for further stoichiometric work
Pour small amount of HCL into both glassware to rinse them
Waste beaker
Some deionized water into graduated cylinder
Volume of needed concentrated solution with cylinder
Volumetric flask using the decanting method
Have to add water first to prevent splashing
To completely get rid of residue that could affect pH analysis