by Dave Brown 3 years ago
279
Alterations of Leukocytes - Copy
by Dave Brown 3 years ago
279

More like this
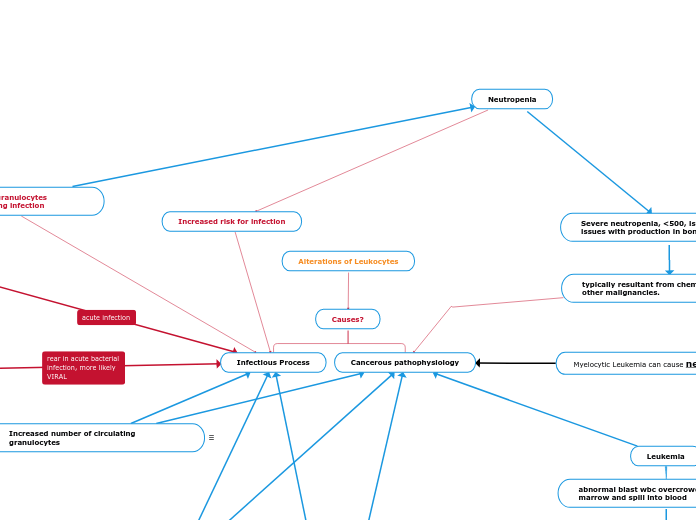
Increased amount of immature neutrophils released into circulation cause a shift to the left. This can be due to either an infectious process, and the body is unable to keep up with production of neutrophils, or from leukemia as well.
Neutrophil count > 100,000, raises blood viscosity significantly increasing chance for thrombosis or complete occlusion of blood vessels.
An increased number of granulocytes is a primary response to an infectious process. However, myeloproliferative disorders such as leukemia can also cause an increase.
Disorders of the white blood cells resulting in levels too low or too high are quantitative, whereas qualitative disorders describe problems with the function of the cell.