by Rosalie Raino Kasi 5 years ago
297
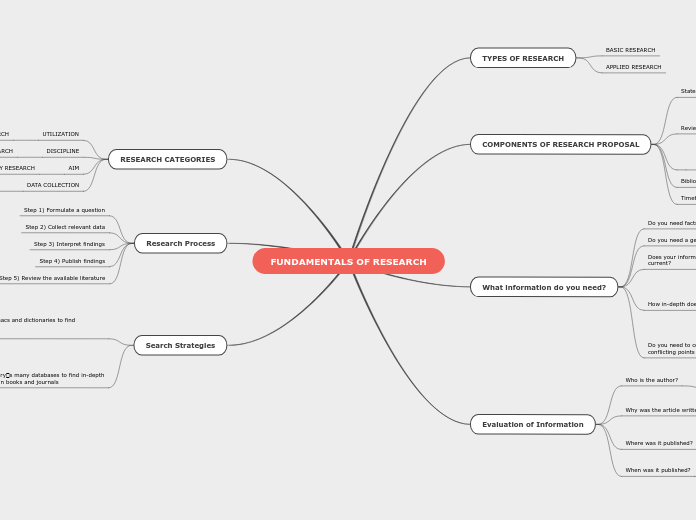
FUNDAMENTALS OF RESEARCH
by Rosalie Raino Kasi 5 years ago
297

More like this
Methodology
subject, design and data correction