by Dara Westrop 1 year ago
175
Sustainable Ecosystems
by Dara Westrop 1 year ago
175

More like this
The Process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration are essential in sustainable ecosystems
During the process of cellular respiration, biotic species convert food energy into chemical energy, which is used to. fuel life processes.
When plants are performing photosynthesis, they transform solar energy into food energy.
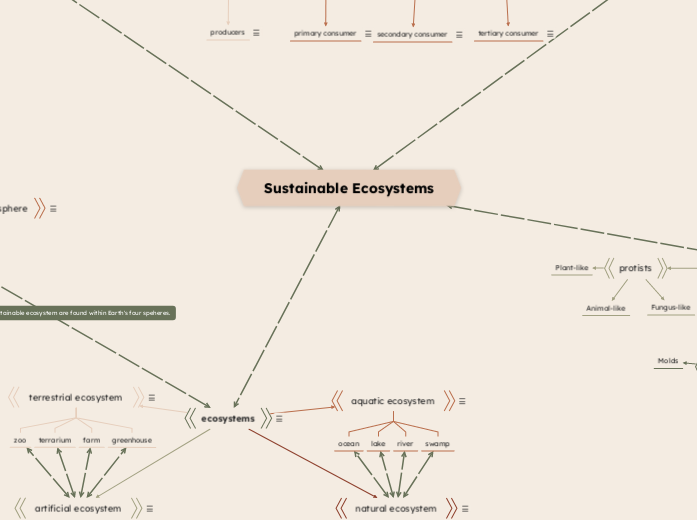
Indicates the feeding level of an organism. Stems from the Greek word "troph," which means feeder.
Heterotroph = other-feeder or consumer. These organisms cannot create their own food and rely on eating other organisms to get energy.
Organisms feed on secondary consumers. They are called tertiary consumers.
Examples:
Organisms feed on the primary consumers. They are called secondary consumers.
Examples:
Organisms are the first to feed on another organism. They are called primary consumers.
Examples:
Autotroph = self-feeder or producer. These organizations can create their own food energy.
Organisms use photosynthesis to create their own food. They are called producers.
Examples:
The regions of Earth where living things exist.
The layer of air above the Earth's surface.
All the water found on Earth, including lakes, oceans and groundwater.
The solid, outer part of the Earth.
Carbon gets recycled using photosynthesis, and the carbon moves from the atmosphere and into living things; when this organic matter respires or decomposes, carbon is sent back into the atmosphere.
Energy flows in a one-way path; organisms that need photosynthesis use energy from the sun to create food energy in the form of glucose; in cellular respiration, this glucose is turned into ATP, which is a molecule with a lot of chemical energy in its bonds.
Communities in a particular area interacting with their abiotic environment.
Man-made structures that are not sustainable and can stop functioning without human help.
A natural ecosystem is one that is found naturally in nature, they are self-sustaining and do not need human help to thrive.
Ecosystems found in water.
Ecosystems found on land.
Biotic populations living and interacting in a particular area.
Bacteria with a corkscrew shape.
Bacteria with a curved-rod-like shape.
Bacteria that have a curved shape.
Bacteria with a rod-like shape.
Bacteria with a round shape.
Plants that creep along the ground and have very fragile, long, thin stems that can't stand tall or support all their weight
Examples
Climbers have very thin, long, and weak stems that can't stand upright, but rather use external support to grow vertically and carry their weight.
Examples
They have very thick, woody, and hard stems called the trunk. This single main stem or trunk gives rise to many branches that bear leaves, flowers, and fruits.
Examples
Short-sized plants with soft, green, delicate stems without woody tissues.
Examples
Medium-sized, woody plants that are taller than herbs and shorter than a tree.
Examples:
Commensalism is an interaction between two species in which only one benefits.
Mutualism is an interaction between two species in which they both benefit.
Competition is a species rivalry for resources such as food, mates, or land.
Fighting for sunlight, space, water, and pollinators.
Parasitism is where a parasite lives with/on/in a host, harming the host species.
Predation is where one species hunts and kills another.