by fatima nikkhou 3 years ago
476
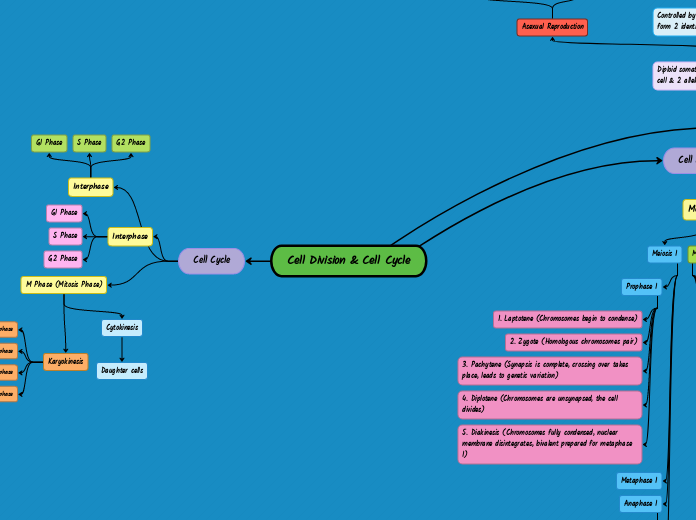
Task 1:Cell Division Concept Map
by fatima nikkhou 3 years ago
476

More like this
In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed
Hydrogen fuel is a zero-emission fuel burned with oxygen.
It can be used in fuel cells or internal combustion engines.
Name the advantages and disadvantages of Hydrogen fuel.
A wind turbine, or alternatively referred to as a wind energy converter, is a device that converts the wind's kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range of vertical and horizontal axis.
Write down the advantages and disadvantages of Wind turbines.
Daughter cells
Telophase
Anaphase
Metaphase
Prophase
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
Sexual Reproduction
Testes, ovaries & anther
Nondisjunction
Eukaryotic
Telophase ll
Anaphase ll
Metaphase ll
Prophase II
Telophase I
Anaphase I
Independent assortment occurs
Metaphase I
Prophase I
5. Diakinesis (Chromosomes fully condensed, nuclear membrane disintegrates, bivalent prepared for metaphase I)
4. Diplotene (Chromosomes are unsynapsed, the cell divides)
3. Pachytene (Synapsis is complete, crossing over takes place, leads to genetic variation)
2. Zygote (Homologous chromosomes pair)
1. Laptotene (Chromosomes begin to condense)
The battery acquires its charged condition either by recharging or in the manufacturing of the unit.
During discharge, the chemical on the anode releases electrons, and ions in the electrolyte undergo an oxidation reaction.
Name the particular compounds in which energy is stored:
Uncontrolled growth/copying = cancer, neurological disorders
Binary fission, DNA is copied & cells divide
Prokaryotic